Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE): A fundamental pillar of modern cybersecurity
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) is a fundamental resource for modern cybersecurity. Maintained by the MITRE Corporation, this standardized and public repository serves to identify and reference security vulnerabilities in software, hardware, and systems. One of the main advantages of CVE lies in its ability to provide a clear and unified nomenclature for vulnerability management, thus facilitating collaboration between researchers, companies, security teams, and regulators worldwide.
What is CVE? A global referencing standard
In an ever-evolving cyber threat landscape, consistent and uniform vulnerability management is essential. Before 1999, the lack of standardization in naming vulnerabilities made coordination between researchers, developers, and security experts complex and error-prone. The introduction of CVE helped overcome this limitation. Here are the major advantages of adopting this repository:
- Standardized communication: The unique CVE identifier eliminates ambiguities by assigning a standard designation to each vulnerability, ensuring a better understanding of security issues.
- Centralized information: CVE becomes an essential reference for documenting vulnerabilities, simplifying risk management and analysis.
- Faster response times: CVE identifiers facilitate correlation with remediation solutions (patches, workarounds, etc.), reducing the time required to address vulnerabilities.
- Global interoperability: As an international standard, CVE ensures interoperability between various cybersecurity tools, whether vulnerability scanners, patch management platforms, or threat intelligence solutions.
Far from being just a database or a rigid standard, CVE is a central communication and coordination mechanism that allows cybersecurity stakeholders to refer to a common vocabulary when discussing critical vulnerabilities. This system has gained particular importance in sensitive sectors like industrial cybersecurity, where undetected vulnerabilities can compromise essential infrastructures. This article highlights CVE's crucial role in threat intelligence and risk management, especially in environments where system resilience is paramount.
Structure of a CVE entry: details and technical references
Each CVE entry is structured around three main elements:
- CVE Identifier: The unique identifier in the format CVE-Year-Number.
- Vulnerability Description: A brief yet precise explanation of the security issue.
- External References: Links to additional resources, such as technical reports, security updates, and related patches.
Example
CVE-2023-12345: A vulnerability in the XYZ module of [Software Name] allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code via insufficient input validation.
Additional information is available in databases such as the National Vulnerability Database (NVD), which enriches each CVE entry with CVSS scores, attack vectors, and specific recommendations. Additionally, organizations such as CERT-FR (the French government's cybersecurity response center) provide alerts and technical bulletins detailing vulnerabilities referenced in CVE.
CERT-FR publishes advisories and practical recommendations to help organizations mitigate risks associated with identified vulnerabilities. This information is particularly useful for security incident management and continuous threat monitoring.
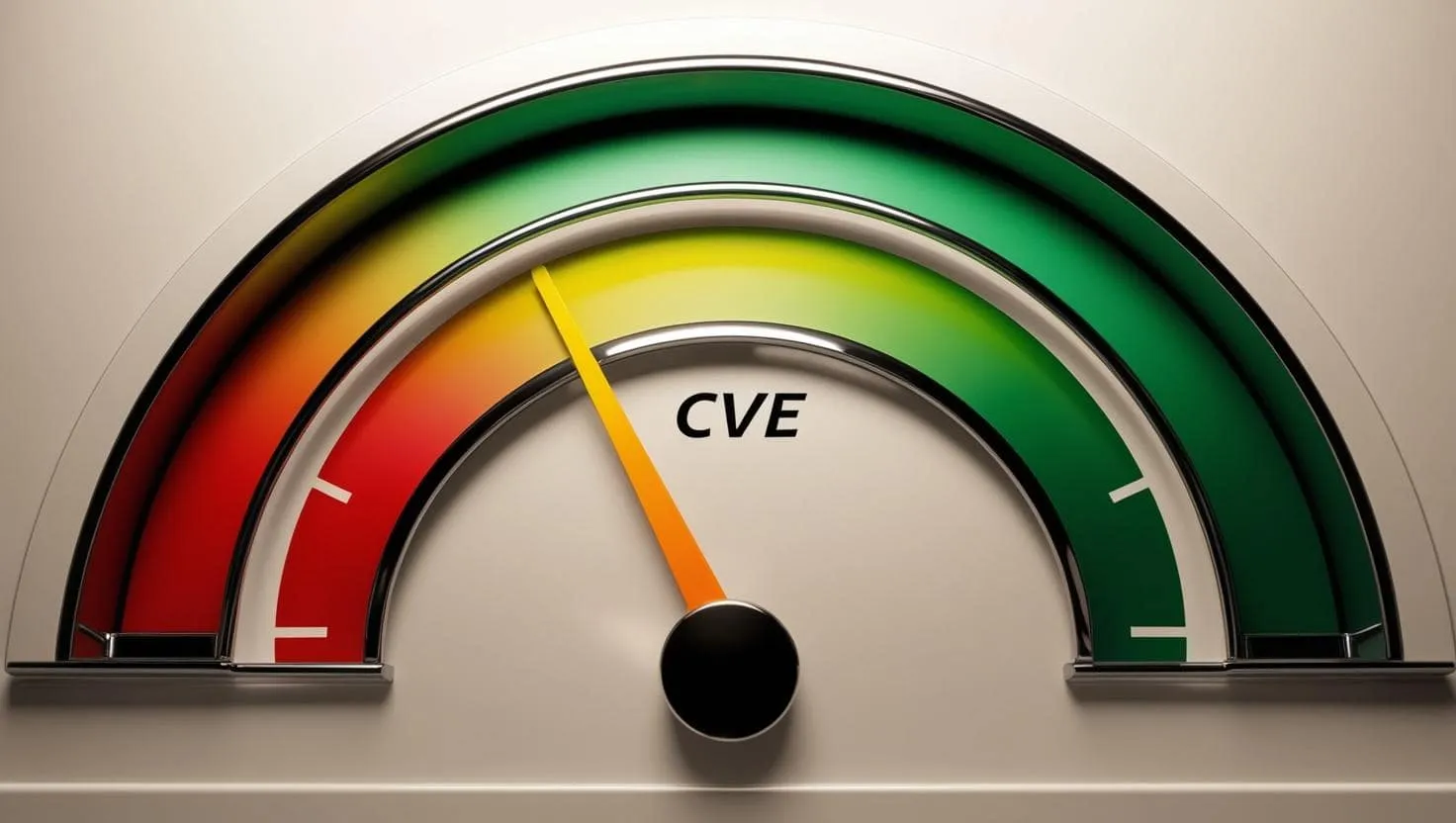

CVSS Scores: evaluating the severity of vulnerabilities
CVSS scores (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) are used to evaluate the severity of vulnerabilities referenced in the CVE. Each vulnerability receives a numerical score that reflects its potential impact and ease of exploitation. CVSS is based on three categories of metrics:
- Base Score : Evaluates the impact and exploitability of the vulnerability, considering criteria such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability impact, as well as exploitation complexity and required privileges.
- Environmental Score : Allows the evaluation to be adjusted based on the specifics of a particular environment (e.g., the criticality of affected systems).
- Temporal Score : Takes into account the availability of patches or workarounds.
The final score, ranging from 0 to 10, classifies vulnerabilities into different severity categories, from low to critical. For example, a vulnerability with a score of 9.0 to 10.0 is considered critical and requires immediate remediation.
Scores are categorized into several severity levels:
- Low (0.1 - 3.9) : Vulnerabilities that present minimal risk. Attacks are difficult to execute, and impacts are limited.
- Medium (4.0 - 6.9) : Vulnerabilities that can be exploited, but with limited or difficult-to-achieve impact.
- High (7.0 - 8.9) : Vulnerabilities that have a significant impact and can be easily exploited.
- Critical (9.0 - 10.0) : Very severe vulnerabilities, often remotely exploitable, with a major impact on the system.
CVSS scores help with vulnerability management by assisting security teams in prioritizing patches. However, the specific context of each organization must always be taken into account for optimal risk management.
CVE and industrial cybersecurity: protecting critical infrastructure
Industrial cybersecurity, involving the protection of industrial control systems (ICS) and critical infrastructure, presents unique challenges. These systems often use legacy technologies or proprietary software that is difficult to update, increasing their vulnerability to attacks.
CVE plays a central role by allowing security professionals to:
- Identify vulnerabilities in industrial equipment : For example, a vulnerability in a Siemens programmable logic controller could be referenced by CVE, with detailed information on the required patches.
- Prioritize remediation actions : In sensitive environments where operational downtime may lead to financial losses or physical risks, CVE helps to rank vulnerabilities by their potential impact.
- Coordinate incident responses : In the event of a cyberattack targeting an industrial network, access to CVE identifiers allows for the rapid identification of exploited vulnerabilities and the deployment of appropriate corrective measures.
- Raise awareness among stakeholders : CVE serves as an educational tool to raise awareness of vulnerabilities among industrial teams and security managers.

The importance of tracking vulnerabilities and updating equipment
Tracking vulnerabilities and regularly updating equipment are imperatives to strengthen cybersecurity. In an environment where threats evolve rapidly, proactive vulnerability management is essential to limit exploitation risks.
- Risk Reduction : Unpatched vulnerabilities represent entry points for cyberattacks. Tracking CVEs allows for quick identification of flaws and the implementation of patches before they can be exploited.
- Prioritization of Patches : Thanks to CVSS scores, vulnerabilities can be prioritized based on their severity and potential impact, allowing critical updates to be targeted first.
- Compliance and Resilience : Tracking vulnerabilities is also required by many regulatory standards and is a fundamental approach to ensure system resilience against cyber threats.
In summary, continuous vulnerability management, based on frameworks like CVE, is key to ensuring infrastructure security and effectively anticipating risks.
We help you track and manage your infrastructure vulnerabilities effectively. Contact us today for proactive risk management.
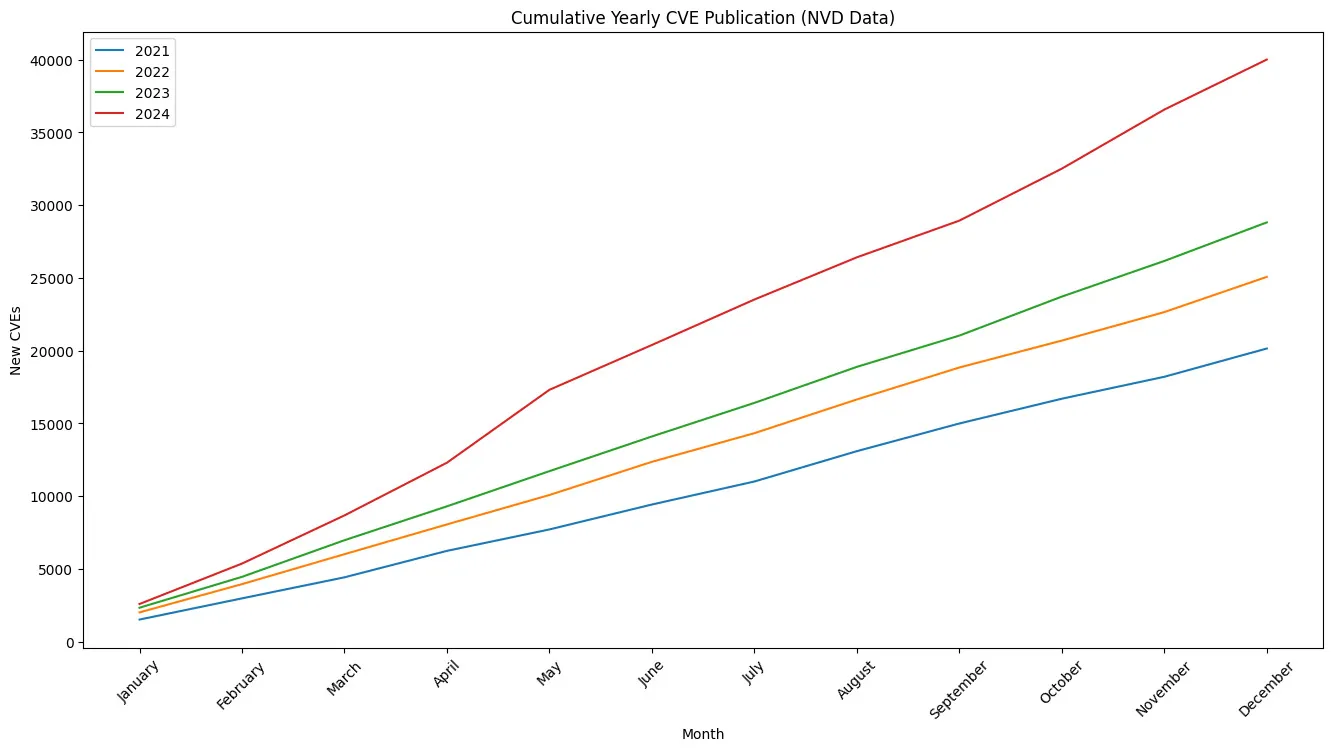
CVE – A significant increase in vulnerabilities
2024 stats
The year 2024 marks a turning point with a record number of vulnerabilities published. Compared to 2023, there is an increase of 38.83% in registered CVEs, confirming a trend toward accelerated discovery of security flaws.
This increase can be explained by several factors:
- Expanding attack surface : The proliferation of connected technologies and cloud services increases exploitation opportunities.
- Improved detection : Efforts by cybersecurity researchers, vendors, and bug bounty programs enable faster identification of vulnerabilities.
- Stricter regulation: Many organizations now require the systematic disclosure of flaws, contributing to the increase in registered CVEs.
In light of this explosion, businesses must strengthen their vulnerability management by prioritizing critical flaws and adopting a proactive approach to mitigate risks.
Conclusion
CVE represents much more than just a database; it is a strategic tool in the fight against cyber threats. By standardizing the identification and management of vulnerabilities, it strengthens collaboration among various cybersecurity stakeholders while facilitating proactive risk management. In an increasingly connected world, adopting CVE is essential to securing critical infrastructures and protecting digital assets.
References
- MITRE CVE Database : https://cve.mitre.org/
- National Vulnerability Database (NVD) : https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln
- CERT-FR : https://www.cert.ssi.gouv.fr/
FAQ
Question 1: What is CVE and why is it important in cybersecurity?
CVE is a public database that provides unique identifiers for each security vulnerability. Its role is crucial for standardizing vulnerability management, facilitating communication among professionals, and accelerating responses to cyber threats.
Question 2: How does CVE help manage vulnerabilities in industrial infrastructures?
In industrial environments, where updates can be complex and costly, CVE allows for quick identification of vulnerabilities and prioritization of remediation actions based on their potential impact.
Question 3: What is the difference between CVE and CVSS?
CVE is used to identify vulnerabilities, while CVSS evaluates the severity of these vulnerabilities by assigning a score that guides remediation priorities.
Question 4: How do businesses use CVE in patch management?
Businesses rely on CVE to associate security patches with specific vulnerabilities, thus enabling rapid and targeted deployment.
Question 5: How is CVE different from CWE?
The CWE (Common Weakness Enumeration) is a classification of design or programming weaknesses that can lead to vulnerabilities. In contrast, CVE lists specific vulnerabilities identified in particular products or systems.
We track your vulnerabilities, contact us.





