Our news
Stay updated on Industrial IoT and cybersecurity with expert advice, tech analysis, and the latest news. Explore insights from DATIVE.

Looking to control your energy consumption and costs while meeting regulatory requirements (CEE, ISO 50001, BACS Decree)? By combining Carlo Gavazzi sensors and meters, the Dupline fieldbus and the DAT’Power Energy Management System, you can turn your site data into clear dashboards, relevant alerts and actionable decisions, delivering a tangible return on investment.

In the pharmaceutical sector, industrial cybersecurity is no longer just about protecting sensitive data. It now underpins the reliability of every medicine produced, the continuity of production, and the trust placed by health authorities. Faced with interconnected OT infrastructures, strict regulatory obligations and critical public health stakes, DATIVE supports manufacturers in securing their critical environments and sustainably improving their operational performance.

A local authority located in Bretagne, operating a wastewater treatment plant made up of six treatment basins, called on DATIVE’s expertise in order to strengthen the cybersecurity of its industrial environment.

In the French Alps, DATIVE supported an inter-municipal authority by delivering a comprehensive OT diagnosis to restore visibility over industrial infrastructures, secure an essential public service, and prepare for NIS2 compliance.

When an industrial network becomes unstable, pharmaceutical production feels the impact immediately. We were engaged to understand, diagnose, and stabilize an environment where each interruption could jeopardize the production of a vital drug. Here is how our team conducted the network audit for a global pharmaceutical leader to restore performance, stability, and cybersecurity.
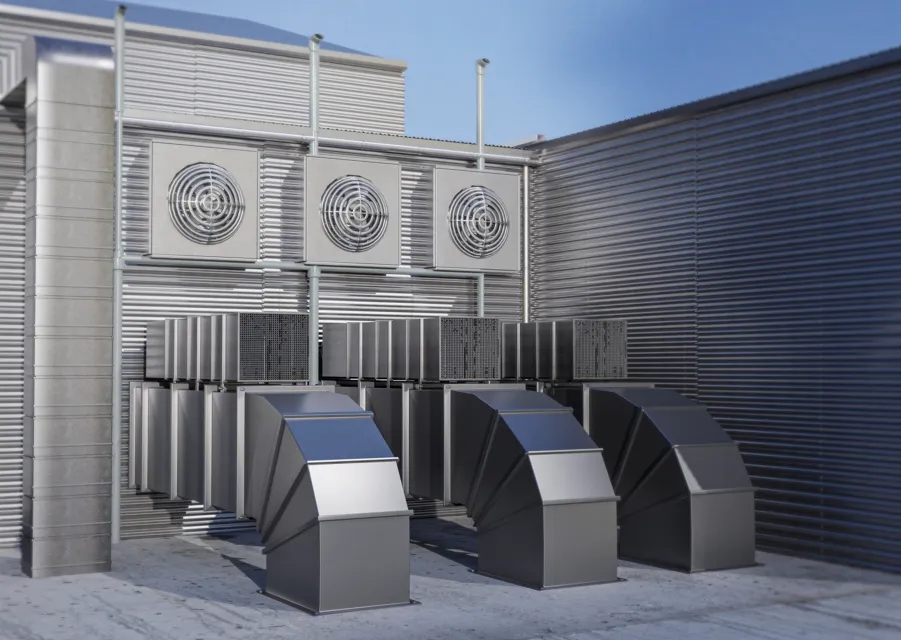

An industrial air-handling system manufacturer selected DAT’Power to structure and optimize its energy management strategy: multi-MES instrumentation, centralized hypervision, and role-specific dashboards. Discover how this project improves responsiveness and strengthens decision-making for energy and maintenance managers.
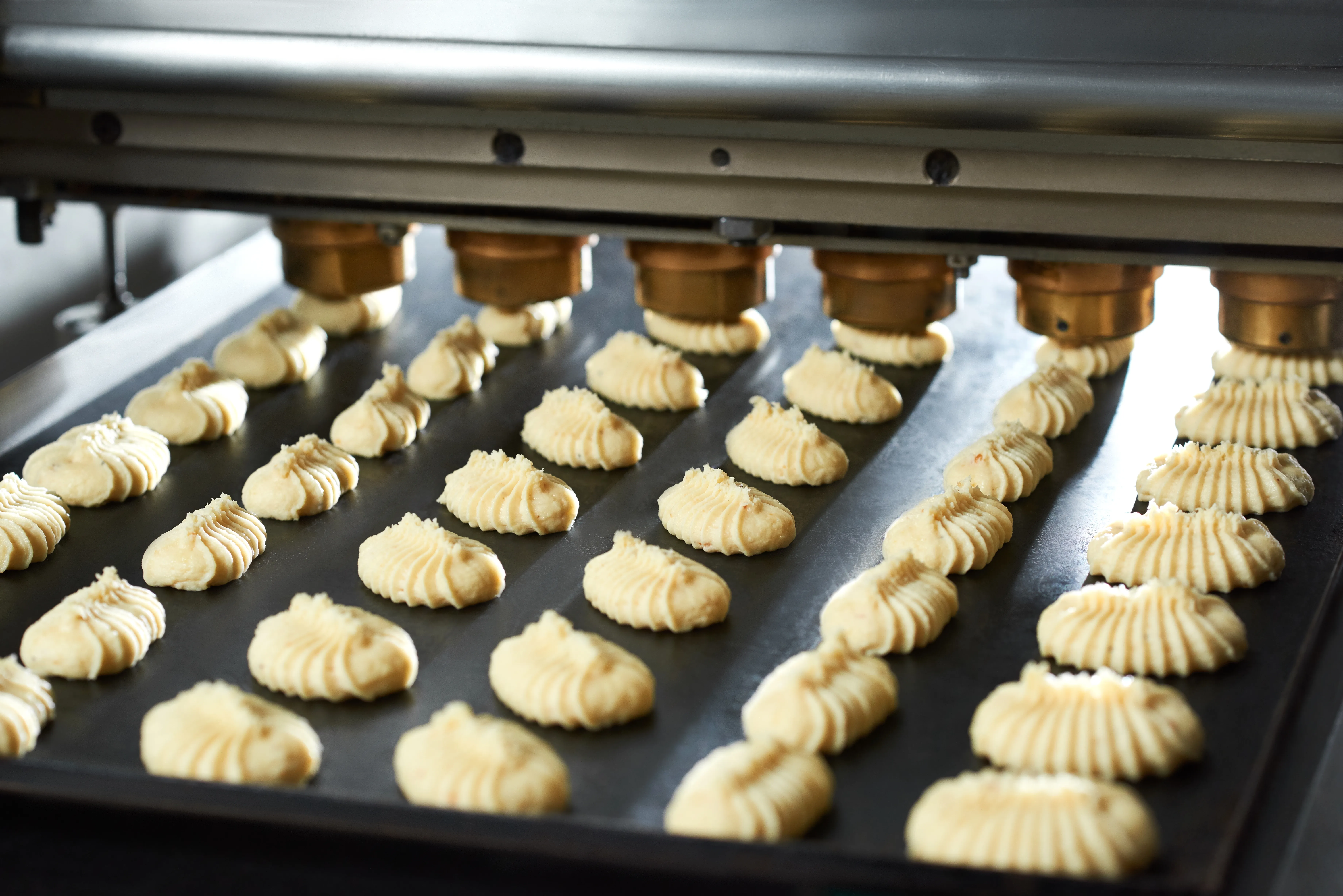

To strengthen cybersecurity and improve the reliability of its OT production network, a major agri-food player based in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region called on DATIVE. The objective was to inventory connected equipment, map the industrial network, and analyze critical communications to strengthen cybersecurity and the resilience of its OT infrastructure.

In a sector as critical as aeronautics, industrial cybersecurity is a major strategic issue. OT systems, which are essential to production, are now exposed to increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. Through a risk analysis based on the EBIOS RM method, DATIVE has supported a major player in the aerospace industry in structuring a robust cybersecurity strategy that complies with regulatory requirements while ensuring continuity of production.

On December 2nd, our DATIVE teams will participate in the Energy for Industry trade show at the Lyon Convention Center. This event, which has become a must-attend for players in the industrial sector, brings together each year experts, suppliers and decision-makers committed to the energy transition
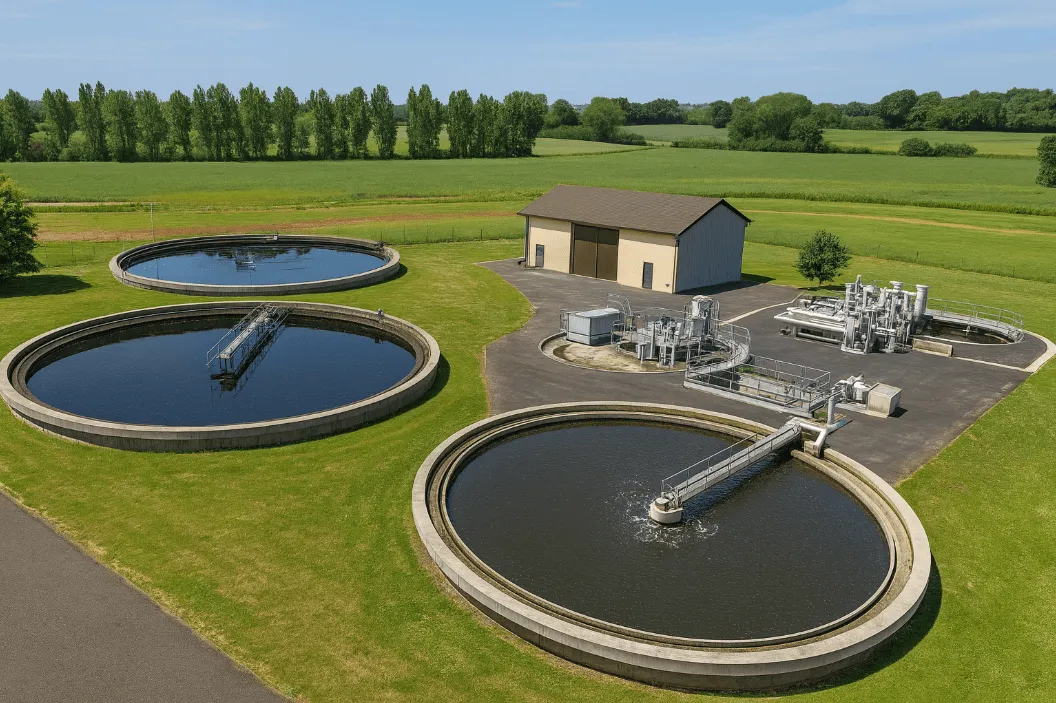

A local authority in Savoie operating around twenty wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) tasked our DATIVE experts with an industrial cybersecurity assessment. Objective: identify OT vulnerabilities, secure the infrastructure, and build a robust action plan to reinforce resilience against cyber threats.

Faced with new cyber challenges, an agri-food manufacturer north of Paris is strengthening the security of its critical workstations with TXOne Stellar Protect sealing, deployed by our DATIVE Cybersecurity experts.

Anonymized 2025 case study: how we deployed DAT’Power on an upper-tier SEVESO site, in controlled phases, to balance HSE, cybersecurity, production continuity and measurable savings.

Developed in the field of nuclear safety to prevent major accidents, defense in depth is now a fundamental concept in industrial cybersecurity. It is based on the idea of successive layers of protection, applied to critical environments, to ensure resilience, security, and business continuity.

Compressed-air leaks weigh heavily on your costs and performance. Discover how DAT’Power detects and alerts in real time, monetizes losses in €/day, and helps you prioritize field interventions with Les Experts GPI—up to predictive maintenance with DAT’Process.

This article presents a comprehensive hardening strategy for obsolete workstations to strengthen your industrial cybersecurity. In industrial environments, we regularly encounter outdated systems (Windows 2000 SP4, XP, 7 or old Windows 10). These systems, although critical in industry, can no longer receive patches: license issues, PLC incompatibilities, or risk of production shutdown.

The Zero Trust model has become a key cybersecurity strategy for OT. This article presents its principles, its benefits for industrial cybersecurity, and the key steps to deploy a Zero Trust architecture adapted to OT network security.

Steam boilers account for a major share of industrial energy consumption. How can you reduce their usage without compromising production reliability? This expert article highlights the key performance indicators to monitor, the right measurement methods, and concrete optimization levers, illustrated with real-world field feedback.

Industrial steam remains a cornerstone of many manufacturing processes. How does a steam boiler work? What are its main uses, and where are the key levers to reduce energy consumption? This article provides a clear, accessible overview of steam boiler operations and practical paths for optimization.

Industrial cybersecurity is no longer optional. With the rise of cyber threats, every industry must build an architecture adapted to its OT systems. An effective strategy relies on a detailed analysis of flows, assets, and risks. This article guides you in designing a robust, scalable, and standards-compliant industrial cybersecurity architecture for 2025.

In a rapidly changing industrial context, availability, performance, and cost control have never been more critical. To address these challenges, one strategy stands out: shifting from corrective to predictive maintenance by leveraging real-world field data.

Industrial cybersecurity has become a major strategic issue today. The rise of IIoT is multiplying the number of connected devices in your industrial environments. At the same time, IT/OT convergence is blurring the boundaries between office and industrial systems. Many devices, often obsolete, remain difficult to secure effectively. As a result, the attack surface of your production environments keeps expanding. Cyber threats are no longer limited to your office systems. They now target your production lines and critical infrastructures as well. Business continuity is directly at risk. A successful attack can halt your production and cause major financial losses for your company. It can also endanger the safety of your production teams, particularly your operators. Your reputation may be damaged, especially in the event of negative media coverage following an attack. In some cases, even national security is at stake, particularly if you are among the operators of vital importance (food, water, energy, …). Faced with these risks, adopting a proactive posture is essential for the sustainability and sovereignty of your industry. This approach protects industrial assets and reduces operational risks. It also ensures the resilience of systems against attacks. This article presents seven key strategies to sustainably strengthen industrial cybersecurity.

SIDO 2025, France’s must-attend event for technological innovation, will take place on September 17–18 at the Cité Internationale in Lyon. DATIVE will be there at booth E142. This year, we will showcase DAT’Power, our flagship energy management solution, along with the expertise of our IIoT cybersecurity division, offering manufacturers a comprehensive, secure, and high-performance approach to digital transformation.

Managing security vulnerabilities in industrial systems has become a key challenge — but one that’s rarely straightforward. With legacy equipment, unpatchable systems, and often incomplete inventories, field teams must navigate significant technical and operational constraints. While standards and frameworks provide valuable guidance, applying them in real industrial environments remains complex. This article explores the real-world obstacles and presents a pragmatic approach to effectively securing existing systems without disrupting operations.

On September 17 and 18, we will be participating in the Lyon Cyber Expo 2025 to defend a cause that is close to our hearts: industrial cybersecurity. Alongside us, FORTINET, a leading technology partner with whom we share the same ambition: to sustainably protect OT environments.

Compressed air is an essential resource for many manufacturers. Used in a wide range of applications-from pneumatic tools to production line automation-it’s often considered the “fourth utility,” after electricity, gas, and water. However, it’s energy-intensive: according to the French ecological transition agency (ADEME), compressed air can account for up to 10% of the electricity consumption of an average industrial site. In some sectors, this share can even reach 30%. Optimizing energy consumption related to compressed air is therefore a key lever for improving overall performance and reducing operating costs. In this article, we’ll explore the challenges of compressed air, key performance indicators, and solutions to improve its energy efficiency.

We are proud to have been recently featured in the magazine Le Jaune et la Rouge, a flagship publication of the Polytechnique alumni community. This article highlights our expertise in industrial cybersecurity within the Gérard Perrier Industrie Group (<a target="_blank" href="https://www.gerard-perrier.com/">GPI</a>) and our practical, field-based approach. This recognition reinforces our belief: <b>securing OT is now a strategic priority for French industrial players.</b>

Industrial cybersecurity attacks are no longer fiction or rare exceptions. From attempted poisoning to power outages, safety system overrides, and global ransomware paralysis, real-world OT attacks are on the rise. These incidents expose critical vulnerabilities in industrial environments and underscore a crucial reality: operational systems have become high-value strategic targets.

Cyber attacks on industrial infrastructures have increased dramatically in recent years. For example, 420 million attacks against critical infrastructures (energy, transport, telecoms) took place between January 2023 and January 2024. This trend can be explained by the emergence of new attack techniques and vulnerabilities in architectures. To remedy this, manufacturers are using trends and tools to help them protect their IoT networks.

In 2024, the industrial sector accounted for 29% of ransomware attacks worldwide. A statistic that illustrates the extent to which connected factories have become prime targets for cybercriminals. Whether opportunistic actors, organised groups or state threats, all are now exploiting technical and human vulnerabilities within industrial environments. Identifying and correcting vulnerabilities has therefore become a strategic priority.
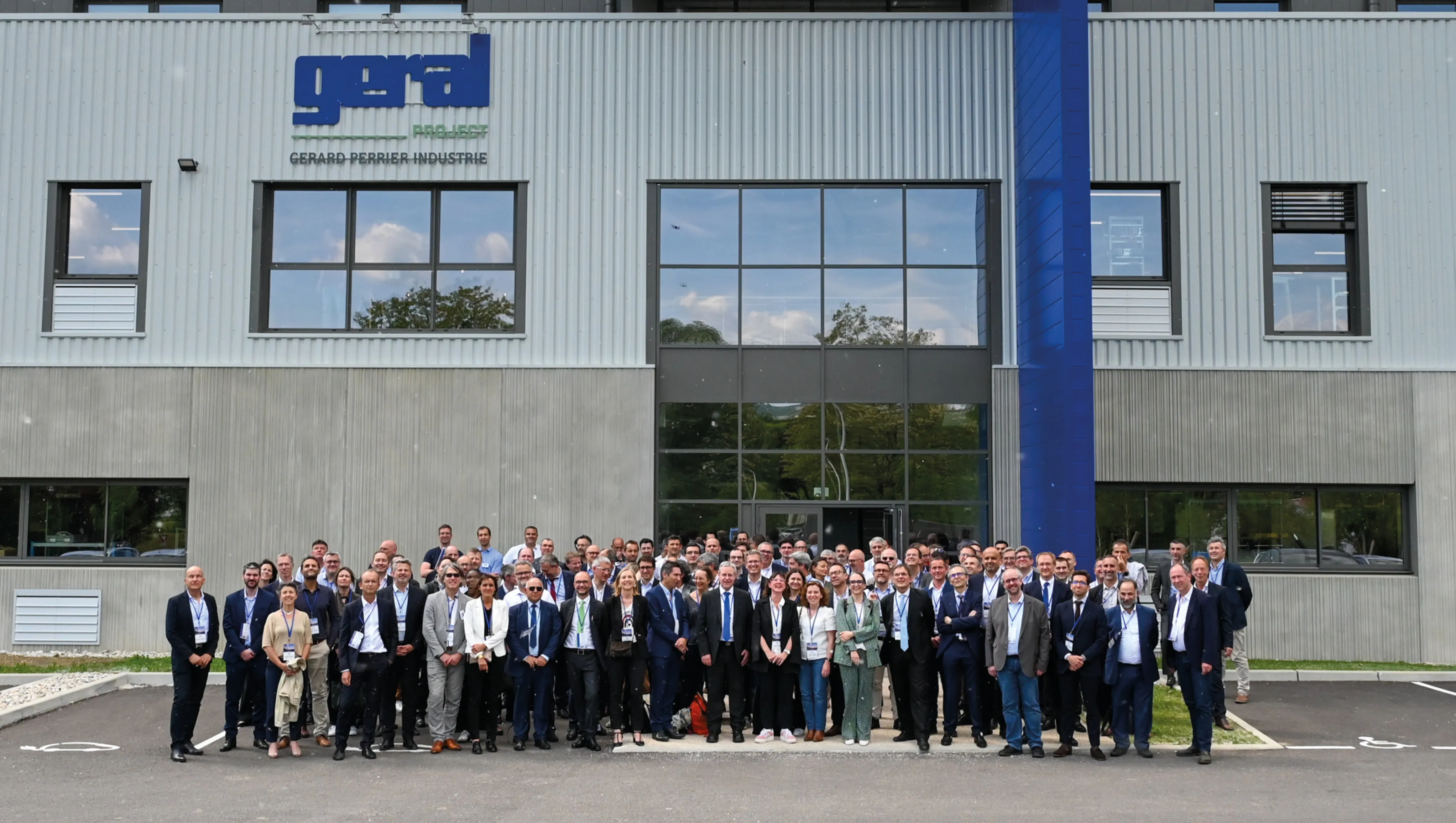

On May 15, the Gérard Perrier Industrie Group had the pleasure of hosting the Cap’Ten & Magellan networks' plenary at its GERAL Manufacturing and GERAL Project sites in Belley (01). The event brought together several EDF Group departments and numerous key players from the nuclear industry—suppliers, major subcontractors, and manufacturers—to discuss safety, industrial performance, and the competitiveness of the French nuclear sector.

The BACS GTB decree requires office and administrative buildings to implement building automation and control systems (BACS) to optimize energy management. What are the objectives of this regulation? Who is affected, and how can compliance be ensured? This article covers everything you need to know about the BACS decree.

The Military Programming Law (LPM) constitutes a central legislative framework for defense and security policies in France. Adopted every five to seven years, it sets the main strategic orientations, financial means, and operational priorities of the French armed forces. The latest version in force, LPM 2024-2030, includes strengthened provisions for cybersecurity, a national priority in the face of the rapid evolution of digital threats. In this article, we will explore the foundations of the LPM, its main provisions, and its impact on industrial cybersecurity, a key area for critical infrastructure and national sovereignty.

The Cyber Resilience Act (CRA), recently adopted by the European Union on March 12, 2024, marks a decisive turning point in the fight against cyber threats facing our increasingly digital society. This regulation aims to establish a robust framework to ensure the cybersecurity of digital products and services by imposing strict requirements on manufacturers, importers, and distributors. By integrating security standards from the design stage of products, the CRA aims to protect not only businesses but also consumers, thereby strengthening trust in the digital economy.

From June 11 to 14, 2025, Paris will host VivaTech, Europe’s largest event dedicated to technological innovation. A true global hub for startups, major corporations, investors, and decision-makers, VivaTech acts as a catalyst for transformation across all sectors. This year, over 165,000 visitors are expected, along with 13,500 startups, 3,500 exhibitors, and 3,200 investors from more than 120 countries.

In a historic move, France has formally accused Russia of orchestrating cyberattacks against its strategic interests between 2015 and 2017, publicly pointing to the GRU and the hacker group APT28.
The rise of Industry 5.0 is transforming industrial environments. This modernization is accompanied by a constantly expanding digital attack surface. Between ransomware, offensive artificial intelligence, and IoT vulnerabilities, threats are becoming more diverse and complex. This article presents an overview of cyberattacks in industrial environments. It also analyzes the main cybersecurity challenges in the short, medium, and long term, based on current technological trends and regulations.

The CER Directive (Critical Entities Resilience), adopted by the European Union in December 2022, establishes a crucial regulatory framework to strengthen the resilience of critical entities against various threats such as cyberattacks, pandemics, and natural disasters. Replacing an earlier directive, it broadens its scope to better protect vital infrastructures that support not only the economy but also the security and well-being of European citizens. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the directive’s implications, objectives, and requirements, offering a clear overview of its impact on organizations and public administrations.

The General Security Regulation for Information Systems (RGS) is a normative framework established to ensure a high level of security for the information systems of French public administrations. Version 2 (RGS V2), the latest update, strengthens this objective by incorporating technical and organizational evolutions tailored to current threats. This article offers a comprehensive overview of the standard, its key requirements, practical applications, and its critical role in the field of industrial cybersecurity, including within essential sectors such as industry.

Join us on April 23rd and 24th, 2025 at ALPEXPO Grenoble – Hall B, Stands B74 & B76

Industry 4.0 is transforming production processes through connected technologies. This evolution enhances the efficiency and flexibility of industrial chains. However, industrial systems are exposed to new threats, highlighting the challenges of industrial cybersecurity. In 2024, 43% of French organizations experienced at least one successful cyberattack. These attacks aim to disrupt operations, steal data, or compromise the security of critical infrastructures. In the face of these growing risks, implementing appropriate cybersecurity strategies becomes essential. This article outlines the main industrial cybersecurity challenges. It presents the risks, impacts, and solutions to strengthen the security of industrial infrastructures.

Critical infrastructures are essential to the smooth running of our modern societies. A failure or targeted attack against these systems could have disastrous consequences. From major economic disruption to threats to public safety. Given the increase in cyber-attacks targeting these infrastructures, industrial cyber-security plays a central role in protecting them. It is based on a set of strict standards and regulations. These aim to strengthen the resilience of industrial systems in the face of digital threats. This report describes the cybersecurity challenges facing critical infrastructures and the main threats they face. It also describes the technical solutions put in place to ensure their protection.

In a world undergoing rapid digital transformation, where even the smallest security flaw can be costly, the ISO/IEC 27005:2022 standard emerges as an essential safeguard for proactive risk management. Combining rigor and adaptability, this framework provides industrial organizations with a structured roadmap to identify, assess, and address threats to their informational assets. In this article, we will break down the key aspects of the standard, its benefits, and how it integrates into a broader security ecosystem.

Since 2004, ENISA, the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (European Union Agency for Network and Information Security), has embodied the ambition to build a secure and resilient digital space. In an environment where cyberattacks are becoming more complex and threats are evolving at a rapid pace, the agency plays a strategic role in actively contributing to the EU's cybersecurity policy. It designs and implements European certification schemes to enhance trust in digital products, services, and processes. In close collaboration with Member States and European institutions, ENISA prepares the continent for future cybersecurity challenges. Additionally, the agency partners with organizations and businesses to strengthen trust in the digital economy, enhance infrastructure resilience, and ensure citizens' digital security. Always vigilant, it promotes knowledge sharing, develops robust structures, and trains future professionals while leading impactful awareness campaigns. The EU Cybersecurity Act has further strengthened its role, solidifying its position as a key pillar in building a trustworthy European cyberspace.

The NIST SP 800-82 standard, published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), is a key guide for ensuring cybersecurity in industrial environments. This document provides valuable recommendations for securing industrial control systems (ICS), including SCADA, DCS, and PLC systems, used in critical sectors such as energy, manufacturing, water, and other essential infrastructures. Due to the increasing cyber threats targeting critical infrastructures, NIST SP 800-82 plays a crucial role in defining best practices to protect industrial systems against cyberattacks. Although this guide is not a mandatory standard, it is widely adopted as a reference by industrial cybersecurity professionals worldwide.
In today’s economic and environmental context, energy performance according to the NF EN ISO 50001 standard is an effective lever for controlling business costs. It helps reduce energy bills and leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions, also enabling organizations to contribute to their environmental and societal commitments. The ISO 50001 standard is therefore a strategic solution for optimizing energy management.

Industry 4.0 is transforming production environments through the connectivity of OT (Operational Technology) systems, SCADA, Industrial IoT, and automated networks. However, this digital transformation also exposes critical infrastructures to increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.

Cybersecurity in industrial environments is a critical issue today. OT (Operational Technology) systems, essential to industry, are prime targets for cybercriminals. Industrial cybersecurity begins by understanding the risks surrounding an industrial infrastructure. This article explores the main OT cybersecurity threats and presents solutions to protect your infrastructure.

The ANSSI framework "Mastering ICS Security for Industrial Systems" is a comprehensive set of best practices designed to guide businesses in managing the security of industrial systems. Published by ANSSI (National Agency for the Security of Information Systems), it is aimed at helping organizations secure their industrial information systems while addressing the unique challenges of these environments. This framework, which falls under industrial cybersecurity efforts, provides specific guidelines for managing industrial control system (ICS) security in sensitive sectors such as energy, water, transportation, and manufacturing. In this article, we outline the content of this framework, its importance for industrial cybersecurity, and the best practices to follow to ensure effective security management.

Adopted in 2022 by the European Union, the NIS2 Directive represents a significant advancement in the field of cybersecurity. Its main goal is to strengthen the resilience of critical infrastructures and harmonize practices across member states. By expanding the scope of the original NIS Directive, it imposes strict requirements aimed at ensuring the continuity of essential services in the face of growing digital threats. This article offers a detailed exploration of the directive, its implications, and its strategic impact.

Adopted in 2016 by the European Union, the NIS Directive (Network and Information Systems) aims to strengthen the security of digital infrastructures. In response to the rise of cyber threats, this regulation imposes strict measures on member states and critical organizations to improve the resilience of information systems. Its goal is twofold: to protect essential infrastructures and promote cooperation among EU countries. Cyberattacks targeting strategic sectors such as energy, healthcare, or transportation are on the rise, threatening service continuity and citizen safety. The NIS Directive seeks to address these vulnerabilities by establishing a demanding regulatory framework for risk management, incident reporting, and coordination of efforts. This article explores its objectives, scope, and practical implications.

Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming energy management in industry. Through connected sensors and intelligent platforms, it enables real-time monitoring, better consumption optimization, and significant cost reduction. How does IIoT improve energy management? This article explores 9 key benefits of this technology for the industry.

In a world where Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing production chains, industrial cybersecurity has become essential. The integration of connected technologies exposes industrial systems, historically isolated, to increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. These attacks can disrupt operations, cause significant financial losses, and jeopardize the sustainability of businesses. This article guides you through best practices and highlights the critical importance of industrial cybersecurity. You will discover why securing your infrastructure is crucial in the face of major risks related to cyber threats. We will provide concrete recommendations to protect your facilities and reduce vulnerabilities in your critical systems. Finally, key solutions will be discussed to secure your sensitive data and ensure operational resilience.

The flagship trade show of the industrial ecosystem will take place from March 11 to 14, 2025, at Eurexpo Lyon. We look forward to meeting you there to discuss key Industry 4.0 topics: optimizing industrial performance through monitoring and control, as well as cybersecurity for industrial sites and processes.

In a context where digital threats continue to grow, organizations must adopt solid approaches to identify, assess, and mitigate cybersecurity risks. The EBIOS Risk Manager (EBIOS RM) method, revised in 2024, stands out as an essential solution. Adopted at the french level or even Europe, this structured method provides a rigorous framework for integrating digital risk management into an organization's overall strategy. This article explores this standard in detail, including its objectives, principles, and practical application.

Cybersecurity is an ever-evolving field, with increasingly complex and sophisticated threats. To better identify, understand, and mitigate system vulnerabilities, the security community relies on standards, frameworks, and tools. One of the most important tools in this context is the Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE). Developed by the MITRE Corporation, CWE is a classification system that groups common software and IT system weaknesses. This article will explore what CWE is, its role in cybersecurity, and its application across various sectors, particularly in industrial cybersecurity, where securing critical infrastructures is essential.

Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) is a fundamental resource for modern cybersecurity. Maintained by the MITRE Corporation, this standardized and public repository serves to identify and reference security vulnerabilities in software, hardware, and systems. One of the main advantages of CVE lies in its ability to provide a clear and unified nomenclature for vulnerability management, thus facilitating collaboration between researchers, companies, security teams, and regulators worldwide.

Industrial control systems (ICS) play a critical role in the operation of critical infrastructures, including key sectors such as energy, transportation, and manufacturing. To protect your industrial infrastructures and prevent financial losses, securing control systems is essential. These cybersecurity solutions ensure productivity and effective protection. Discover the importance of industrial control systems, the challenges they face, and practical cybersecurity solutions.

Industrial cybersecurity is a critical challenge for companies across all sectors, particularly those operating in sensitive industrial environments such as automotive, energy, healthcare, and critical infrastructure. In this context, implementing robust cybersecurity standards and frameworks is essential to protect information systems, sensitive data, and industrial equipment from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. One of the most widely adopted cybersecurity frameworks is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), which provides a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks. This article offers a detailed overview of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, its components, and its application in the field of industrial cybersecurity.

The ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard, a global reference for information security management, defines a framework for implementing an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It helps protect sensitive data, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, availability, and traceability. Applicable to all organizations, it enables the identification of threats, risk management, and enhances resilience against cyber threats. The 2022 version incorporates simplified controls and measures adapted to modern technologies, such as the cloud.

In an interconnected world where the convergence of industrial and IT systems increases risks, the international standard IEC 62443 emerges as a key framework for securing Industrial Automation and Control Systems (IACS). Essential for protecting critical infrastructures (energy, transportation, manufacturing), it offers a unified approach addressing vulnerabilities, access, communications, and countermeasures. By involving manufacturers, integrators, and operators, IEC 62443 strengthens system resilience against growing cyber threats.

Industrial infrastructures have become prime targets for cyber attacks. Often orchestrated by malicious actors, including state-sponsored groups. The impact of these attacks can be devastating, both operationally and financially.Anticipating cyber attacks on industrial infrastructures means putting in place solid defences. This article guides you through the risks, solutions and best practices for securing your systems.
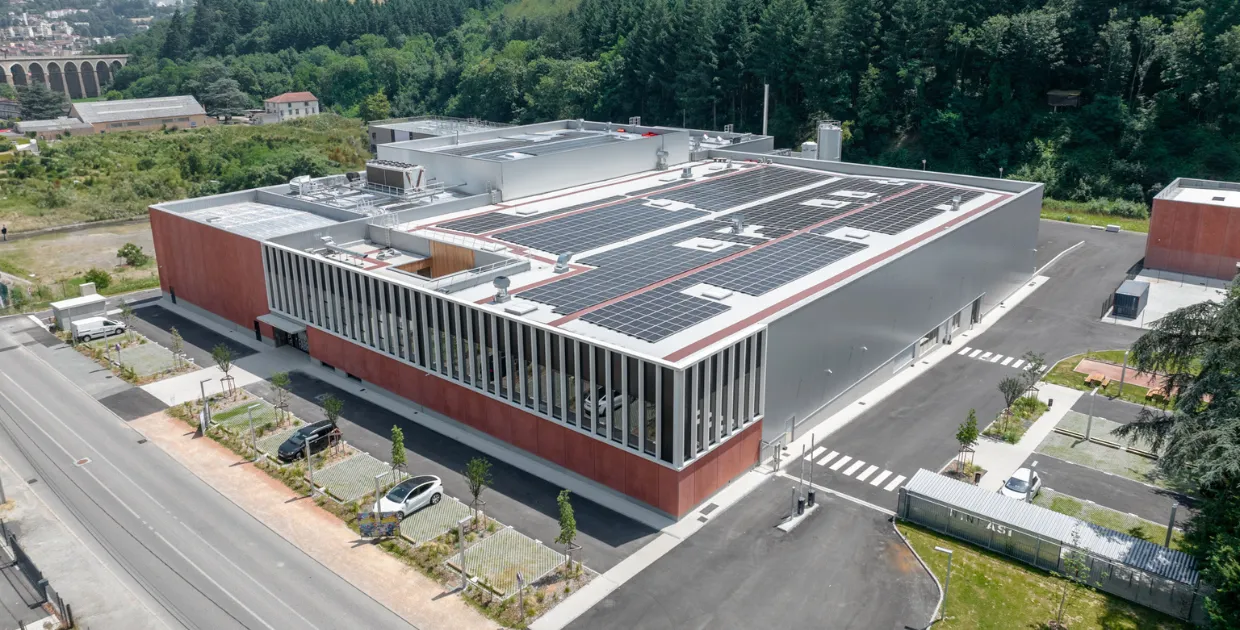

Discover how DATIVE transformed the energy efficiency of NINKASI's new production site with a complete solution, integrating ERP production data, energy usage instrumentation, and intelligent alarms. A turnkey project that delivered savings within the first months while ensuring rigorous energy performance tracking.

DATIVE helps you anticipate drought restrictions and monitor water consumption and effluents in real time. Discover how our solutions can support your sustainable and compliant water resource management.

In an industrial context where operational challenges multiply, managing data and ensuring its security have become priorities. Companies face fragmented systems, obsolete equipment, and an increasing need for energy optimization. The goal is not just to collect data, but to integrate it efficiently for decision-making and action.
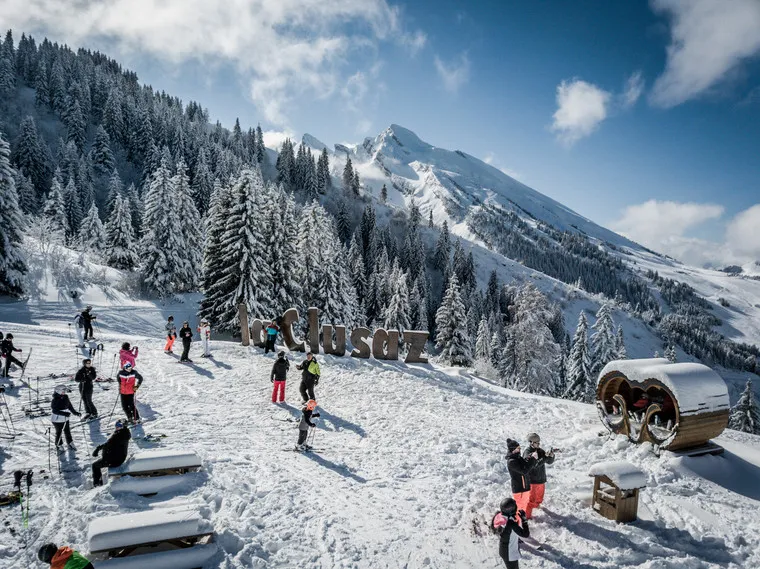

In the face of climate change challenges, ski resorts must adopt innovative strategies to reduce their carbon footprint. La Clusaz has chosen to rely on the DAT’Mountain solution, developed by DATIVE in collaboration with SEIREL, to improve its energy management while providing a quality customer experience.

In the era of industrial digital transformation, the innovative integration of industrial IoT solutions is crucial for business success. In this context, DATIVE emerges, recently honored by the prestigious Manufacturing Technology Insights magazine, not only for its excellence in industrial digitalization but also for its significant contribution to industrial optimization through IoT.

Since its appearance in 2019, Lockbit 3.0 has been one of the most formidable ransomware programs in the digital world. With over 1700 attacks listed worldwide since 2020, including renowned companies such as Thales, Continental and TSMC, its presence poses a serious threat to organizations IT security.

As part of our ongoing commitment to strengthening our customers' industrial cybersecurity, DATIVE is delighted to announce a new strategic partnership with WALLIX, France's leading identity and access management (IAM) solution. This collaboration marks another step forward in our mission to provide cutting-edge solutions in the face of growing threats.

The Décret Tertiaire is a decree that can have a significant impact on industrial companies, whether you own tertiary buildings or are wondering about your potential subjection to this decree. In this article, we will delve into the specific aspects of the Décret Tertiaire for industrial companies, and provide you with the essential information to understand and meet this regulatory obligation.

A new directive (Network and Information Security, version 2), more ambitious than the first measure, was adopted in January 2023 by the Parliament & Council of the European Union to further protect companies against cyber threats. It will come into force in France in the second half of 2024 at the latest.

We are proud to announce that DATIVE has recently joined the French'Fab community, a dynamic movement that celebrates French industrial excellence and innovation. This marks an important milestone for our company and reinforces our commitment to helping develop the French industry of tomorrow by being at the forefront of industrial innovation.

The LoRa (for “Long Range”) network can be used to generate private networks with secure and encrypted communication. This means that the data is controlled, it remains with the company (locally), and it does not depend on a wireless provider. The range between the transmitter and the receiver is 500 metres (the record being more than 40 kilometres), which enables the entire industrial site to be covered with just a few antennas and provides redundancy in the event of faults. The installation is less costly and simpler to implement than a wired solution. The devices can operate off batteries, with a battery life of around five years.

AI-generated text has revolutionised the way in which users interact with computers and digital devices, enabling them to carry out complex tasks more rapidly and more efficiently than ever before. However, its use can also present risks for the security of data and of industrial secrets.