International Standard IEC 62443: Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Cybersecurity
In an interconnected world where the convergence of industrial and IT systems increases risks, the international standard IEC 62443 emerges as a key framework for securing Industrial Automation and Control Systems (IACS). Essential for protecting critical infrastructures (energy, transportation, manufacturing), it offers a unified approach addressing vulnerabilities, access, communications, and countermeasures. By involving manufacturers, integrators, and operators, IEC 62443 strengthens system resilience against growing cyber threats.
What is the IEC 62443 Standard?
The IEC 62443 standard consists of a series of technical documents aimed at standardizing and improving the cybersecurity of industrial control systems. These documents cover a wide range of topics, from basic cybersecurity principles to specific requirements for hardware and software components, as well as organizational processes to follow.
Key Objectives:
- Protect critical infrastructures: The standard aims to mitigate risks associated with cyber threats by securing industrial systems and networks.
- Standardize cybersecurity practices: It defines common requirements for manufacturers, integrators, and users to establish consistent and effective processes.
- Ensure robust and scalable cybersecurity: The standard enables businesses to implement security measures that evolve with threats and technologies, adapting to new market demands.
Target Audience
The standard addresses a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Industrial Operators: Responsible for managing critical systems and ensuring operational continuity.
- Technology Providers: Manufacturers of hardware and software components for industrial systems.
- System Integrators: In charge of designing and implementing industrial solutions.
- Regulatory Authorities: Ensuring the protection of critical infrastructures.
Expected Impact of Compliance
- Risk Reduction: A significant decrease in the likelihood of successful attacks and their associated impacts.
- Improved Resilience: Enhanced ability to maintain stable operations despite cyber incidents.
- Increased Trust: Greater credibility with partners, customers, and regulators.
What is the IEC 62443 Standard?

Scope of Application
The IEC 62443 standard is designed to meet the security requirements of industrial systems across a wide range of contexts. Its application spans various sectors such as healthcare, energy, manufacturing, and public infrastructure. In healthcare, for example, it ensures the protection of connected medical devices and hospital systems. In the energy sector, it helps secure electrical grids as well as oil and gas facilities. Automated production lines in manufacturing benefit from these principles, as do water transport and distribution systems in public infrastructure.
This standard is intended for industrial operators, technology providers, and integrators, who play a key role in implementing complex multi-vendor systems. Its scope is not limited to physical equipment; it also encompasses software, virtual components, and operational processes.
From a geographical perspective, IEC 62443 has a global scope, although it can be adapted to meet local regulatory requirements. It provides a detailed technical framework for the design, operation, and maintenance of industrial automation and control systems, ensuring uniform and consistent application across different contexts and regions.
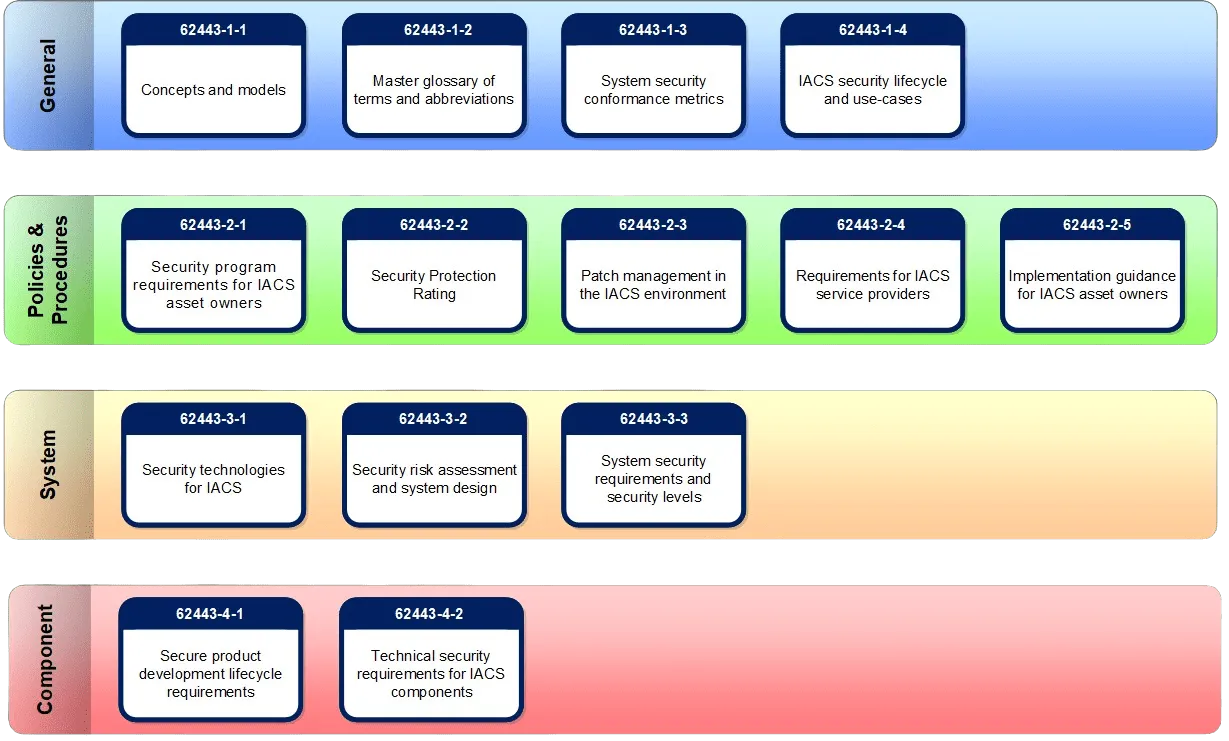
Structure of the IEC 62443 Standard
The IEC 62443 standard is structured into several sections that address specific aspects of the cybersecurity of Industrial Automation and Control Systems (IACS):
- General Policies and Procedures (62443-1-x): Definition of essential concepts and foundations for applying the standards, including terminology and the cybersecurity maturity model.
- Asset and Process Management (62443-2-x): Requirements for the management of critical assets and processes, including risk management, security controls, and compliance auditing.
- Systems (62443-3-x): Covers the design, installation, and maintenance of security systems in industrial environments, with technical requirements for securing industrial control architectures.
- Components (62443-4-x): Technical requirements for individual components of industrial systems, including devices and software, with a focus on secure development processes and component security.
Why IEC 62443 is Essential for Industrial Cybersecurity
Strengthening the Security of Industrial Systems
Modern industrial systems are interconnected, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks. IEC 62443 helps identify and address vulnerabilities specific to these environments, thus ensuring the security of the entire infrastructure. This standard applies to all stakeholders involved in the design, installation, and operation of industrial control systems.
Standardizing Cybersecurity Practices
One of the major advantages of IEC 62443 is that it provides a consistent and internationally recognized framework. This allows the various players in the value chain, such as integrators, technology providers, and industrial operators, to speak a common language when it comes to cybersecurity and implement coherent processes to reduce risks.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
IEC 62443 addresses the growing need for regulations and cybersecurity standards in industrial sectors. Increasingly, governments and organizations are imposing compliance requirements with standards like IEC 62443 to protect critical infrastructures from cyber threats. This includes requirements for regular security audits and documentation of cybersecurity controls.
Implementing IEC 62443: Key Steps
Risk and Needs Assessment
The first step in implementing IEC 62443 is conducting a risk assessment. This involves understanding the specific threats to industrial systems and determining the security levels required for each zone and component. This analysis allows for the definition of an appropriate security strategy and the prioritization of actions.
Defining Security Levels (SL)
The IEC 62443 standard introduces four security levels (SL), each corresponding to a required degree of protection for a given system or zone. These levels are defined as follows:
- SL 1 - Protection against accidental threats : At this level, systems are protected against human errors and accidental incidents. This includes basic measures like access management and regular data backups.
- SL 2 - Protection against opportunistic attacks : Systems at this level are protected against attacks by malicious actors with limited resources. This includes stricter access controls, intrusion detection systems, and vulnerability management.
- SL 3 - Protection against moderately targeted attacks : SL 3 protects against more sophisticated attacks by attackers with significant technical resources. Measures include continuous monitoring systems, behavioral analysis tools, and advanced defense mechanisms.
- SL 4 - Protection against sophisticated targeted attacks : This is the highest security level, designed to protect against attacks by highly organized cybercriminal groups or state actors. This level requires the most advanced security controls, physical protection measures, and highly specialized incident response processes.
Implementation of Security Controls
For each security level, IEC 62443 defines specific security controls. This includes access management, system monitoring, communication protection, and encryption of sensitive data. These controls are crucial to ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of industrial systems.
Audit and Continuous Improvement
Once the security controls are implemented, regular audits should be conducted to ensure their effectiveness and identify potential improvements. IEC 62443 encourages a continuous improvement approach, with periodic reassessment of threats and vulnerabilities.
Best Practices
To ensure sustained compliance with IEC 62443, the following best practices are recommended:
- Network Segregation : Establish distinct security zones to separate industrial networks from traditional IT networks.
- Access Control and Identity Management : Limit access to industrial systems to authorized personnel only and ensure that each user has the minimal access level required to perform their tasks.
- Regular Maintenance and System Updates : Perform regular security updates on all systems and equipment, including software and hardware.
- Intrusion Detection Mechanisms : Use solutions to monitor and detect any suspicious activity on industrial networks.
- Resilience Planning : Develop resilience strategies to cope with cyberattacks, including business recovery and operational continuity plans.
Relationship with Other Standards
Complementary or Related Standards
The IEC 62443 standard integrates smoothly with other international cybersecurity standards. For example, ISO 27001, which focuses on information security management, complements IEC 62443 by providing a comprehensive management framework for protecting sensitive data and information systems.
Comparison with Other Standards
Although IEC 62443 shares certain principles with other cybersecurity frameworks, it stands out primarily for its focus on industrial control systems (ICS) and the protection of critical infrastructures. Unlike standards such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, which is more generic and applicable to a wide range of organizations and sectors, IEC 62443 offers specific requirements tailored to industrial environments. It addresses in detail the technical, organizational, and procedural aspects necessary to protect industrial control systems from cyber threats, making it particularly relevant for sectors such as energy, transportation, and industrial production.

Evolution and Current Trends
Version History
IEC 62443 was introduced in 2007 to address the growing need for cybersecurity in industrial control systems. Successive versions have incorporated updates to keep pace with evolving threats and technologies. The 2018 version updated requirements for complex architectures, and the 2023 version strengthened the consideration of risks related to the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and the convergence of IT and OT systems.
Future Trends
Key trends for the future include:
- Cybersecurity of Industrial IoT (IIoT) : The increasing number of connected devices in industrial settings is pushing the standard to focus on securing connected objects.
- IT and OT Convergence : The growing interconnection of IT and industrial systems will require adjustments to the standard to enhance security in these hybrid environments.
- Cloud and Hybrid Environments : With the growing use of the cloud in industrial infrastructures, IEC 62443 may specify security requirements for these new environments.
The 2023 version of IEC 62443 reflects these changes and positions the standard as an essential framework in the face of future cybersecurity challenges in the industrial sector.
Resources and References
Here are the sources we used to create this guide on IEC 62443:
- Official IEC 62443 Text
- Practical guides such as EBIOS RM for risk analysis
- Publications from ENISA and ANSSI on industrial cybersecurity
- Tools and frameworks like CWE/CVE for vulnerability management
Conclusion
IEC 62443 is a fundamental standard for ensuring the cybersecurity of industrial systems. By establishing rigorous processes, clear technical requirements, and standardized practices, it plays a crucial role in protecting critical infrastructures from growing cyber threats. Adopting this standard represents a strategic lever for enhancing the security of industrial systems, ensuring their resilience against the rapid evolution of cyberattacks.
By adhering to the defined security levels and implementing appropriate controls, industrial organizations can not only mitigate risks but also maintain the continuity of their operations in the face of increasingly complex digital threats. In short, IEC 62443 stands as an indispensable reference for any industrial organization seeking to optimize its security and effectively prepare for future challenges. It is important to be well-supported, and DATIVE can assist you in compliance and securing your installations.
Need assistance with IEC 62443 compliance? Contact our experts today!
FAQ
What is the difference between IEC 62443 and other cybersecurity standards?
IEC 62443 is specifically focused on the cybersecurity of industrial systems, while other standards like ISO 27001 are more broadly applied to information security management across various sectors.
Is IEC 62443 applicable to small businesses?
Yes, although the requirements may seem complex, IEC 62443 offers solutions tailored to different levels of risk and business maturity, including small businesses.
Who needs to comply with IEC 62443?
Companies managing critical infrastructures, such as those in energy, transportation, or industrial production sectors, as well as industrial control technology providers, must comply with IEC 62443. It also applies to integrators and operators of industrial control systems.
What are the costs associated with complying with IEC 62443?
The cost of compliance can vary depending on the size and complexity of the industrial infrastructure. It typically includes costs for audits, training, system security updates, and implementing cybersecurity controls.





