NIS2 Directive: A Pillar of Cybersecurity in Europe
Adopted in 2022 by the European Union, the NIS2 Directive represents a significant advancement in the field of cybersecurity. Its main goal is to strengthen the resilience of critical infrastructures and harmonize practices across member states. By expanding the scope of the original NIS Directive, it imposes strict requirements aimed at ensuring the continuity of essential services in the face of growing digital threats. This article offers a detailed exploration of the directive, its implications, and its strategic impact.
Objectives of the Standard
Main Objectives or Purposes
The NIS2 Directive aims to address the growing sophistication of cyber threats and proactively protect critical infrastructures. Its objectives include harmonizing cybersecurity requirements among member states, strengthening the resilience of organizations providing essential services, improving incident management to reduce their impact on operations, and encouraging enhanced cooperation among member states to combat cross-border cyberattacks.
Target Audience
The NIS2 Directive establishes specific criteria to determine the entities concerned, notably essential and important businesses. These criteria are primarily based on:
- Sector of activity
- Number of employees
- Revenue
Competent authorities, such as the ANSSI in France, also have the ability to designate specific entities based on additional criteria.
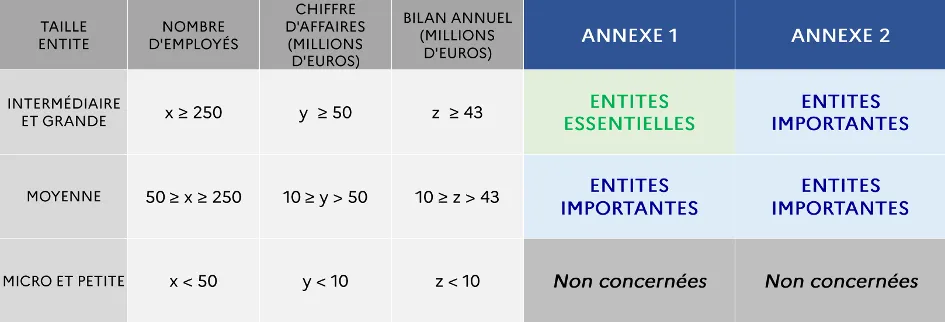
Essential Entities (EE)
Essential entities are generally medium to large-sized businesses operating in the sectors defined in Annex 1 of the directive. They must meet one of the following threshold criteria:
- Number of employees greater than or equal to 250
- Annual revenue greater than or equal to 50 million euros
- Annual balance sheet greater than or equal to 43 million euros
Important Entities (EI)
Important entities are those that do not meet the criteria defining essential entities. By default, any entity not falling into the category of essential entities will be considered an important entity.
Are you ready for NIS2? Contact DATIVE for a complete compliance audit.
Expected Impact of Compliance
Compliance with NIS2 promises better protection against cyberattacks through robust policies, reduced service interruptions for critical infrastructures, and increased trust from business partners and customers in digital systems.
Scope of Application
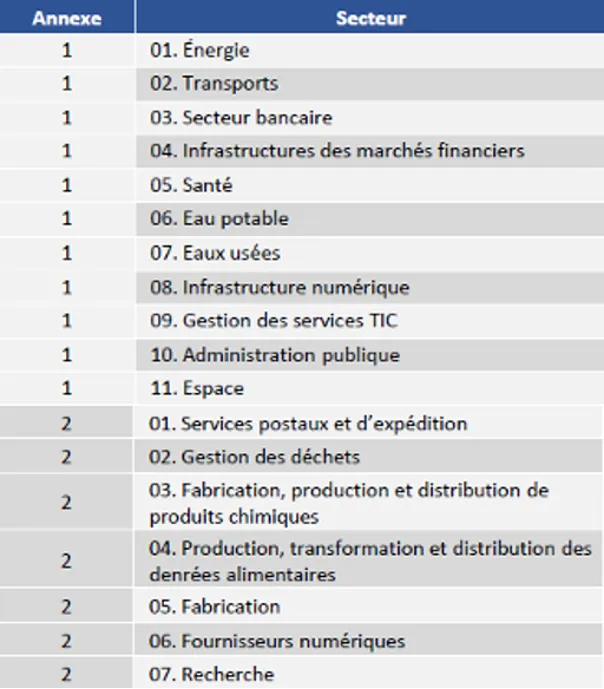
The NIS2 Directive substantially broadens the scope compared to its previous version, covering a wider range of sectors deemed critical for the security of infrastructures and services. It now includes traditionally sensitive sectors such as energy, transport, and telecommunications, but also extends to essential fields such as:
- Health: With particular attention to hospitals, clinics, and laboratories, which are key players in managing health crises and protecting health data.
- Digital infrastructures: This includes data centers, cloud services, and communication networks, which play a central role in the global digital economy.
- Financial services: This category includes banks, payment institutions, market infrastructures, and other players in the financial sector, which are vital elements for economic stability and transaction management.
This extension of sectors aims to better protect the critical links in interconnected supply chains, which can be prime targets for digital attacks, and to strengthen overall resilience against cyber threats. The image below illustrates the affected sectors and the interconnections between these strategic domains.
Overview of the Main Themes or Chapters of the Standard
Cybersecurity Governance
The directive imposes a direct responsibility on business leaders for cybersecurity, including the establishment of a clear risk management policy and the obligation to report to the competent authorities on the security status.
Risk and Incident Management
Entities concerned must implement rigorous processes to identify and assess risks, monitor emerging threats, and document and report any significant incident within the prescribed timeframes.
Cross-Border Cooperation
A central pillar of NIS2 is the increased collaboration among member states, embodied by the exchange of information on threats and incidents and the implementation of coordinated responses to major cyberattacks.
Implementation and Compliance
Key Steps for Compliance
Compliance begins with an initial risk assessment to identify specific vulnerabilities. Organizations must then develop a cybersecurity strategy incorporating technical and organizational measures and invest in training and awareness to strengthen internal capabilities.
NIS2 puts your cybersecurity to the test. Entrust DATIVE with the compliance of your industrial systems.
Best Practices
- Use the ANSSI's IT Hygiene Guide: Implement the 42 security measures proposed by ANSSI, a simple and effective first step to strengthen security and start complying with NIS2.
- Conduct regular audits: Perform cybersecurity audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure continuous compliance monitoring.
- Adopt recognized frameworks: Use frameworks like ISO 27001 or the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to structure risk management in a solid and sustainable manner.
- Collaborate and share information: Participate in threat-sharing networks to exchange information and strengthen collective defense, an effort that requires a longer investment but is essential.
Resources and Tools Available to Support Organizations
Organizations can take advantage of guides from ENISA, risk assessment tools, threat intelligence platforms, and European grants dedicated to cybersecurity.
Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with the obligations imposed by the NIS2 directive can lead to substantial financial penalties. The fines depend on the category of the entity concerned:
- For essential entities: A minimum fine of €10 million or 2% of annual turnover.
- For important entities: A minimum fine of €7 million or 1.4% of annual turnover.
These sanctions aim to encourage organizations to comply with cybersecurity requirements and ensure the protection of critical infrastructures against cyber threats.

Relationship with Other Standards
Complementary or Related Standards
ISO/IEC 27001: Information Security Management System (ISMS)
- A key standard for cybersecurity risk management.
- Complements NIS2 by defining requirements for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an ISMS.
EU Cybersecurity Act
- A framework for the certification of cybersecurity products and services at the European level.
- Helps demonstrate compliance with NIS2 requirements, especially for critical sectors.
- Provides a risk-based approach to cybersecurity management.
- Aligned with NIS2 on incident management, digital resilience, and critical infrastructure protection principles.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- Pertains to the protection of personal data, with requirements for security and incident management.
- Complements NIS2 on securing sensitive information and notifying security breaches.
Comparison or harmonization with other standards
NIS2 vs ISO/IEC 27001
Both standards align with risk management and cybersecurity of networks and information systems. However, their approach differs: ISO/IEC 27001 provides a certifiable framework for information security management, allowing companies to receive official recognition of their compliance. In contrast, NIS2 imposes binding legal obligations, making compliance mandatory for affected organizations.
NIS2 vs EU Cybersecurity Act
NIS2 aims to strengthen digital resilience and risk management of critical infrastructures by imposing strict requirements on strategic businesses. The Cybersecurity Act focuses mainly on the cybersecurity certification of products and services, ensuring their reliability before being marketed. Additionally, this certification helps secure technologies used in critical infrastructures covered by NIS2.
NIS2 vs NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
Although NIS2 and NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) share common goals such as risk management, digital resilience, and incident response, their approaches differ. NIST CSF offers a flexible and adaptable framework, allowing organizations to tailor their cybersecurity strategies based on their needs. In contrast, NIS2 imposes strict obligations, especially for critical sectors, leaving less room for adaptation according to context.
NIS2 vs GDPR
The GDPR and NIS2 pursue distinct yet complementary objectives. The GDPR focuses on personal data protection, imposing strict rules on the processing and storage of sensitive European citizens' information. NIS2, on the other hand, targets the cybersecurity of critical infrastructures, ensuring that these entities implement solid measures to protect their systems. Both regulations overlap on the security of sensitive information and incident notification obligations, thereby strengthening the overall protection of data and infrastructures.

Evolution and Updates
History of Versions or Recent Updates
The evolution of NIS:
- NIS1 (2016): The first EU cybersecurity directive, adopted in 2016, aimed at enhancing the resilience of networks and information systems by imposing security and incident management obligations on operators of essential services and digital service providers.
- Proposal of NIS2 (2020): In response to the rapid evolution of digital threats, the European Commission proposed a revision of NIS1 to expand the scope and strengthen cybersecurity requirements, including additional sectors such as digital infrastructures, health, and financial services.
- NIS2 (2022): The NIS2 directive was adopted in December 2022, replacing NIS1. It introduces stricter requirements for cybersecurity in critical sectors, with enhanced risk management obligations, better cooperation between member states, and harsher penalties for non-compliance.
- Implementation (2023-2025): EU member states had until October 2024 to transpose the NIS2 directive into their national legislation. By 2025, the implementation of NIS2 in member states continues, with EU monitoring to ensure uniform and effective application.
Thus, in 2025, NIS2 is fully in force, and member states must have integrated the requirements into their legislation, with the EU monitoring the effectiveness and compliance of cybersecurity measures across Europe.
Future Trends
There is an expected increase in the integration of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity tools, as well as a rise in the requirements for third-party vendors in supply chains.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits for Businesses or Organizations
The directive provides enhanced resilience against cyberattacks, improves regulatory compliance by reducing the risk of sanctions, and strengthens competitiveness through increased trust from partners and customers.
Challenges or Limitations
However, the initial costs of compliance can be high, particularly for SMEs. Additionally, the complexity of technical requirements may demand specialized skills that are difficult to mobilize.
Don’t let NIS2 catch you by surprise. Plan your compliance now.
Resources and References
- NIS2 Directive: Official text of the EU cybersecurity directive.
- ISO/IEC 27001: International standard for information security management.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: US framework for cybersecurity management.
- EU Cybersecurity Act: Regulation on cybersecurity product and service certification within the EU.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): EU regulation on personal data protection.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the NIS2 Directive represents a major turning point in the cybersecurity of critical infrastructures in Europe. It imposes stricter requirements and governance aimed at ensuring the resilience of essential sectors against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. While compliance may seem complex, it offers both enhanced protection and an opportunity to strengthen trust with partners and clients. Companies must therefore act now to assess their risks and prepare to meet the new obligations.
FAQ
Question 1: What is the NIS2 Directive?
The NIS2 Directive is a European Union legislation aimed at strengthening the cybersecurity of critical infrastructures and digital services.
Question 2: Which sectors are affected by NIS2?
Critical sectors such as energy, healthcare, transportation, and digital infrastructures are directly targeted.
Question 3: What are the consequences of non-compliance?
Non-compliant organizations risk significant financial penalties and a loss of trust from their partners.
Question 4: How to align with the NIS2 Directive?
By adopting appropriate governance, strengthening risk management, and collaborating with the relevant authorities.
Question 5: Does the NIS2 Directive replace the NIS Directive?
Yes, it is an expanded version tailored to current cybersecurity needs.





