How does industrial cyber security protect critical infrastructure?
Critical infrastructures are essential to the smooth running of our modern societies. A failure or targeted attack against these systems could have disastrous consequences. From major economic disruption to threats to public safety. Given the increase in cyber-attacks targeting these infrastructures, industrial cyber-security plays a central role in protecting them. It is based on a set of strict standards and regulations. These aim to strengthen the resilience of industrial systems in the face of digital threats. This report describes the cybersecurity challenges facing critical infrastructures and the main threats they face. It also describes the technical solutions put in place to ensure their protection.
What is critical infrastructure?
Definition
By definition, a critical infrastructure is a set of systems essential to the smooth running of a company. It relies on industrial control systems to supervise and automate various industrial processes.
These systems mainly include:
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) ;
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers) ;
- HMI (Human Machine Interface).
Industrial control systems control industrial operations.
For more information on how it works and the to secure industrial control systems, read our article Industrial control systems: importance, challenges and solutions !
The sectors concerned
The critical infrastructures cover from many sectors have been identified as vital to a country's security and economy. The NIS2 directive classifies these infrastructures in two categories:
- EE (Essential Entities) ;
- EI (Important Entities)
The ANSSI (Agence Nationale de la Sécurité des Systèmes d'Information) has identified 18 sectors. These sectors are the first to be concerned by these regulations, to reinforce their cybersecurity. These 18 sectors are classified into 2 appendices, with appendix 1 taking precedence over appendix 2:
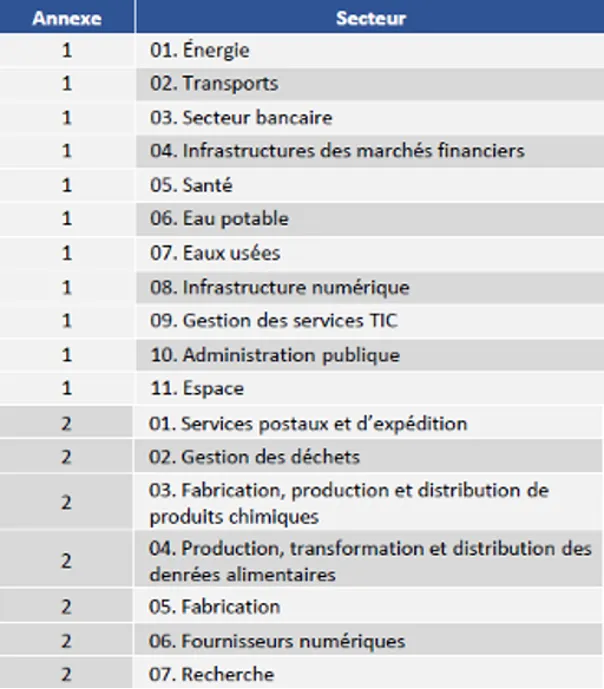
Every sector relies on digital systems and that require increased protection against cyber threats.
The importance of critical infrastructures
Critical infrastructures support the essential functions of a country, guaranteeing stability and continuity of services. A failure can have a cascading effect on other strategic sectors.
They are priority targets because of their strategic value. Their interdependence makes them vulnerable to major disruptions. An attack on a single entity can affect an entire network.
The resilience of critical infrastructures determines the continuity of vital services. Low fault tolerance exposes a country to major interruptions. Enhancing their robustness helps mitigate the risks associated with crises and unforeseen disruptions.
Cybersecurity for critical infrastructures
Multiplication of cyber attacks over time
Cyber attacks on critical infrastructure have risen sharply in recent years. Between 2019 and 2021, industry moved from the 8ᵉ to the 2ᵉ most targeted sector. This increase is the result of the adoption of industry 4.0. This trend has pushed industrial equipment towards digital transformation, improving the productivity and profitability of manufacturing processes.
However, industrial control systems within the critical infrastructures are more exposed to cyber attacks. The interconnection of IT (information technology) and OT (operational technology) systems considerably increases network's attack surface. Industrial equipment is thus exposed to new vulnerabilities.
In 2023, 60% of all cyberattacks against critical infrastructures were carried out by state-run groups. These attacks seek to weaken a country's stability by paralyzing its essential networks.
Infrastructure regulations reviews
Critical infrastructures often encounter to establish an effective cybersecurity strategy. They lack resources, specialized expertise and visibility of best practice. Standards enable infrastructures to evaluate and structure this approach. At the same time, they guarantee a consistent and effective approach. Adopting common standards also helps to reduce protection gaps in the face of a given benchmark. Standards may come from different bodies, applying to different regions of the world. Exclusively French standards exist, as do European and international standards.
These infrastructures are subject to regulations strict cybersecurity standards. Key standards include:
- NIS2: strengthens network and system security risk management. Involves strict measures against cyber attacks
- IEC 62443: defines security standards for industrial control systems. Protects equipment and networks from internal and external threats
- ISO/IEC 27001: provides a management framework for information security. Ensures the protection of data and systems
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: provides recommendations for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to and restoring the security of critical infrastructure.
These regulations guarantee the resilience of critical infrastructures in the face of cyber threats.

Threats to critical infrastructures
The cybersecurity threats to critical infrastructures continue to increase. This increase can be explained by the evolution of attack techniques and the rise of industry 4.0. Interconnected technologies further expose networks to cyberattacks and increase the risk of compromise. A successful attack can cause service and financial losses. Beyond that, they can also cause national security breaches.
Cybercriminals, state groups and hacktivists, target these infrastructures for a variety of reasons. They can economic, strategic or simply destabilizing:
- Physical sabotage of OT equipment: destruction or manipulation critical equipment to cause breakdowns or service interruptions
- Malicious code injection on control systems: tampering with industrial software to disrupt production processes
- Manipulation of sensors and actuators: sending false data to control systems to cause operational errors
- Attacks on industrial wireless networks: exploiting flaws in Wi-Fi or Bluetooth protocols to intercept or modify communications.
Find out more about threats in the sector industrial, see our article Cybersecurity threats in OT environments.

The importance of industrial cybersecurity for the critical infrastructure protection
Industrial cybersecurity is essential for guarantee the smooth operation of critical infrastructure. Increasing threats expose these infrastructures to attacks with major consequences. Securing industrial systems helps prevent targeted cyberattacks and avoid service interruptions. But also to protect strategic equipment. Why is industrial cybersecurity so important? Three major axes explain its importance.
Protection against targeted cyber attacks
Critical infrastructures are targets cybercriminals, hacktivists and nation-states. For the latter, cyberattacks are a strategic tool for destabilization. Sabotaging critical infrastructure can weaken a country, disrupt its economy or compromise its security. Strengthening industrial cybersecurity can prevent such intrusions and protect sensitive data. From a national point of view, security helps preserve national sovereignty.
Preventing service interruptions and financial losses
A cyber attack can paralyze an critical infrastructure, bringing operations to a halt. The financial consequences can be catastrophic. From lost production to high remediation costs. A cybersecurity strategy to limit these risks and ensure continuity of service.
Contact our DATIVE experts for a strategy of effective, long-lasting cybersecurity!
Safety in industrial control systems
The critical infrastructures are based on technologies such as SCADA, HMI and PLC to supervise their operations. These systems, originally designed without IT security, are now vulnerable to cyberattacks. Reinforcing their protection secures industrial processes and prevents malicious manipulation.
5 steps to protecting critical infrastructure
The protection of critical infrastructures is essential to ensure the continuity of industrial operations. A structured five-step approach allows you to effectively strengthen your industrial cybersecurity.
Step 1: Identify/map your network
Before securing a critical infrastructure, it's essential to know all the assets connected to your network. Making an inventory of your equipment enables you to assess the surface area exposed to cyber threats. A detailed cartography identify critical interconnections and data flows. Without this global view, it is impossible to apply tailor-made and effective protection measures.
DATIVE offers mapping and inventory services to establish a precise inventory of your industrial network.
Protect your infrastructure by contacting our experts
Step 2: Assess your security level
A security assessment establishes the current state of protection of a critical infrastructure. This analysis is based on two key phases:
- Constat: identification of vulnerabilities, analysis of network configurations, examining security protocols and policies. This stage detects vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers,
- Remediation: establishment of appropriate recommendations to reduce identified risks. This includes strengthening access and network protection. But also the correction of vulnerabilities and the improvement of cybersecurity practices
Our assessment services offer a precise diagnosis and targeted corrective actions to secure your infrastructure.

Step 3: Implementing security solutions
Implementing security solutions tailored to the constraints of each critical infrastructure is essential. Tailor- made security solutions provide effective, proactive protection.
These security solutions can reinforce different parts of the critical infrastructure. Reinforcing access control is a first layer of security within the organization. Network security solutions are essential to protect industrial control systems from cyber threats. Knowing your critical equipment and its vulnerabilities is the key to maintaining it in a operational/security condition (MOC / MCS). Other, more complex solutions enable you analyze and regulate flows within your infrastructure.
The implementation of these solutions consultation with cybersecurity experts.
Contact us for support throughout your production line!
Step 4: Continuously protect your infrastructure
In addition to securing your architecture, it's essential to ensure its longevity. This means regularly updating protective measures. Cybersecurity never stops, trends accelerate and threats multiply. Every day, new vulnerabilities appear that could impact your industrial control systems.
Continuous protection enables to anticipate and counter these attacks before they cause any damage. From a regulatory point of view, continuous protection ensures compliance and avoids penalties.
A security incident can damage a company's reputation. Demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity builds trust with customers and partners.
For all these reasons, it is essential to maintain its critical infrastructure at a high level of safety.
Step 5: good network security practices
Equipment security is essential, but the human factor remains a major source of cyber attacks. Within critical infrastructures, it is common to have outside personnel. These personnel, as well as operators and technicians, must comply with the good practice policy.
The ANSSI is putting in place a guide to best practices to be followed for controlled security. These best practices include:
- Set up a policy. Select complex passwords, difficult to guess or find with automated tools ;
- Get to know your users and service providers. Staff accessing their private space are subject to different rights and accesses. It is essential to define administrator and user rights for computer workstations. Set up procedures for staff arrivals and departures. Each account must be kept up to date. A user account that no longer belongs to the company must be deactivated
- Carry out regular backups. One of the best practices to follow is the 3-2-1 rule. This technique involves creating three copies of your data, storing them on two different types of media, and keeping one copy off-site.
For more information on good practices to apply in industry, see our article here : Good practices in industrial cybersecurity: tips and importance!
Conclusion
Critical infrastructures are the backbone of modern society, indispensable to our daily lives. A failure or targeted attack against these systems could lead to catastrophic consequences. From major economic disruption to threats to public safety. Against this backdrop, industrial cybersecurity is an essential bulwark against the increasing number of cyberattacks. It is based on a set of rigorous standards and regulations. These standards aim to strengthen the resilience of industrial systems against digital threats.
By investing in cybersecurity, we ensure not only the continuity of your essential services, but also the security and prosperity of our societies. But also the security and prosperity of our societies.
Cyber attacks wont wait for you. Secure your industrial infrastructures !





