Industrial Control Systems: Importance, Challenges, and Solutions!
Industrial control systems (ICS) play a critical role in the operation of critical infrastructures, including key sectors such as energy, transportation, and manufacturing. To protect your industrial infrastructures and prevent financial losses, securing control systems is essential. These cybersecurity solutions ensure productivity and effective protection. Discover the importance of industrial control systems, the challenges they face, and practical cybersecurity solutions.
What is an industrial control system?
Definition of an industrial control system
By its definition, an industrial control system refers to all the equipment and technologies present in industrial environments. They optimise the efficiency of the production line. They also provide supervision and guarantee the safety of the industrial process.
These technologies mainly include the following systems:
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition);
- HMI (Human Computer Interface);
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers).
The operation of an industrial control system
An industrial control system is based on the automation of manufacturing processes. Sensors collect data in real time to automatically adjust production parameters. Programmable automata run predefined programs to monitor and manage industrial equipment. This enables continuous monitoring and rapid response to variations in operating conditions.
Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) provide complete visibility of the status of the production line. They display real-time data to inform on the status and performance of industrial control systems. Operators can adjust parameters via the interface to optimise production operations. Visual and audible alerts quickly signal any malfunctions or anomalies detected.

The importance of an industrial control system for your business
Industrial control systems offer several advantages guaranteeing the efficiency of the production line. These include automation, monitoring and equipment management. But also cost reduction and anticipation of breakdowns. Let's find out more about these benefits.
Improved operational efficiency
Industrial control systems ensure optimum efficiency through the use of different types of systems. These systems provide real-time data to optimise production. They include PLCs and intelligent sensors. These sensors can be of various types: temperature, position, pressure vibrations, etc.
HMIs provide operators with direct control and continuous monitoring of industrial control systems. SCADA systems supervise and control processes while collecting data in real time. They enable centralised management and analysis of data, guaranteeing rapid response to anomalies.
These technologies mean that the industrial process is largely automated and controlled. Human error is reduced. Decision-making is optimised, encouraging continuous process improvement.
Enhanced security
Industrial control systems use sensors to monitor hazardous environments in real time.
Programmable logic controllers and SCADA systems reduce the need for manual intervention in production, and enable sensitive areas to be monitored remotely. They also enable sensitive areas to be monitored remotely.
On the production floor, alarms are also generated to warn operators immediately. Despite unavoidable human intervention, these systems improve operator safety.
The implementation of predictive maintenance
Industrial control systems enable more predictable maintenance through data collection. They monitor the condition of equipment in real time to detect signs of failure.
Sensors identify potential problems before they affect production operations. Operators can then plan preventive maintenance and avoid unscheduled stoppages. The data collected also enables maintenance intervals and times to be optimised. Optimising the productivity of the production line.

Regulatory compliance
The regulations ensure that every company complies fully with national and international laws. These laws have been established for various reasons: operator safety, product quality, respect for the environment, etc.
The industrial control systems facilitate compliance with these regulations. Automatically generated reports simplify audits and inspections, ensuring complete traceability of operations. High-risk environments are controlled and automated, reducing the risk of accidents. Real-time data monitoring ensures compliance with pre-established standards.
These systems limit non-compliances and, consequently, the risks of sanctions.
6 challenges facing your industrial control systems
1. IT security
The increasing interconnection between IT (information technology) and OT (operational technology) systems further exposes industrial control systems to cyber attacks. Connected to the Internet, these systems become targets for malware, ransomware and other malicious actions. This interconnection significantly increases their exposure rate, estimated at between 86% and 93% depending on the case.
2. Obsolescence
Many industrial control systems are still operating with obsolete operating systems and firmware. Because of their essential availability, these systems are often not updated regularly. This increases their vulnerability to cyber attacks. And reduces their ability to meet modern security and performance requirements. As a result of their interconnection with IT, these systems are also exposed on the Internet. The rate of exposure is rising sharply.
Obsolescence is a major challenge for your industrial infrastructure.
3. Insecure protocols
The use of insecure protocols is a major threat to industrial control systems. Some protocols, still in use today, do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanism. However, these protocols are essential for industrial communications between equipment. Among the best-known protocols are Telnet, Modbus, VNC, BACnet. Malicious users can thus intercept and manipulate sensitive information leading to serious industrial consequences. These consequences can include production interruptions and alterations to critical processes. But also incidents endangering the physical safety of employees and infrastructures.

4. Lack of supervision
The lack of surveillance is a major challenge in the industry, especially when it comes to safety.
The lack of log centralisation tools prevents incidents from being analysed quickly and efficiently. The system logs contain fundamental information for detecting anomalies, but they remain dispersed. Without centralisation, events are difficult to correlate, delaying the detection of potential attacks. This increases the risk of unidentified cyberattacks, affecting infrastructures and industrial production.
Centralised monitoring tools enable events to be analysed in real time for a rapid response. Without these tools, problem detection and resolution become reactive, not proactive. This exposes industrial control systems to prolonged intrusions, with impacts on security and profitability.
5. Access management
In industry, user sessions are sometimes left open for extended periods. This is due to a need to simplify certain repetitive tasks and speed up processes. It is also common for weak passwords to be configured, not complying with security policies. In some cases, passwords may be written down on visible media to make them easier to remember.
Managing user accounts can also be complex. Some accesses are not always revoked quickly. Some accounts remain active even after the operators have left. Even in the case of external service providers or one-off users, resulting in security risks.
Access to industrial control systems should be segmented according to responsibilities and levels of control required. These practices can introduce vulnerabilities into industrial control systems, with potential security impacts. The consequences of these flaws can range from compromised security to production stoppages and financial losses.
6. Absence of antivirus software
The absence of antivirus on servers and workstations leaves industrial control systems vulnerable to cyberattacks. Without anti-virus, these systems are a gateway for malware and ransomware. Without antivirus, it is difficult to detect and prevent threats. These attacks can lead to production breakdowns and loss of sensitive data. But also abnormal behaviour, leading to security risks for employees and infrastructures. It is estimated that 90% of industrial control systems are exposed to these risks.

For more information about securing your industrial infrastructure, contact us.
Solutions to protect your industrial control systems
Protecting industrial control systems has become essential in the face of increasing cyberthreats. These threats can lead to production stoppages, deterioration in quality and corruption of sensitive data. The consequences are multiple and critical to industrial processes.
In order to guarantee the integrity, availability and confidentiality of industrial operations, it is essential to integrate appropriate security solutions at all levels.
Securing physical access
Physical access control is one of the first lines of defence in securing critical installations. It aims to restrict access to sensitive areas and equipment to authorised people only. This includes not only access to physical areas, such as server rooms and electrical cabinets. But also direct access to the equipment itself (servers, industrial control systems, network equipment).
The use of access cards and badges on an industrial site makes it possible to authenticate and control individuals accessing these areas.
On network equipment, the use of port shutters blocks physical access to unused ports. These shutters are only effective if the port is also disabled. Thus preventing any network flow passing through that port.
Asset inventory
A complete asset inventory is essential for understanding and controlling your industrial infrastructure. Without visibility of your equipment, it is impossible to define a perimeter to effectively protect your industrial control systems. This inventory must also be kept up to date throughout the company's activity for optimum efficiency.
Contact us for more information about our tailor-made services
Securing assets
Securing assets is about defining a stable configuration and optimal behaviour of an industrial control system, in order to detect possible malicious behaviour in the future. This can include implementing station sealing solutions. The operating state of a system is saved as a reference. Sealing is based on the "white list" principle. Only previously approved software, programs and utilities are allowed to run. Any attempt to add a process that does not comply with this white list is detected and analysed. This blocks the execution of malicious software that could compromise industrial control systems.
Network segmentation
The Purdue Model is a security architecture for industrial control systems. Each type of system is separated into distinct hierarchical levels. Each level constitutes an equipment-specific criticality level. They have defined accesses, limiting unauthorised interactions between the different parts. This segmentation reinforces the overall security of the network, preventing unwanted or malicious access. This model is divided into 5 distinct layers:
- Level 0 - Sensors and actuators: This level includes equipment that collects data in real time and acts on the physical environment,
- Level 1 - Controllers (PLC): These are the PLCs and controllers that execute actions based on the data collected by the sensors,
- Level 2 - SCADA Supervision: This level is dedicated to supervision systems that monitor and control industrial processes remotely,
- Level 3 - Production control: This includes industrial control systems that manage and optimise production processes at a strategic level,
- Level 4 - Operations Management: This level covers the management of business operations, including planning and data analysis at an administrative level.
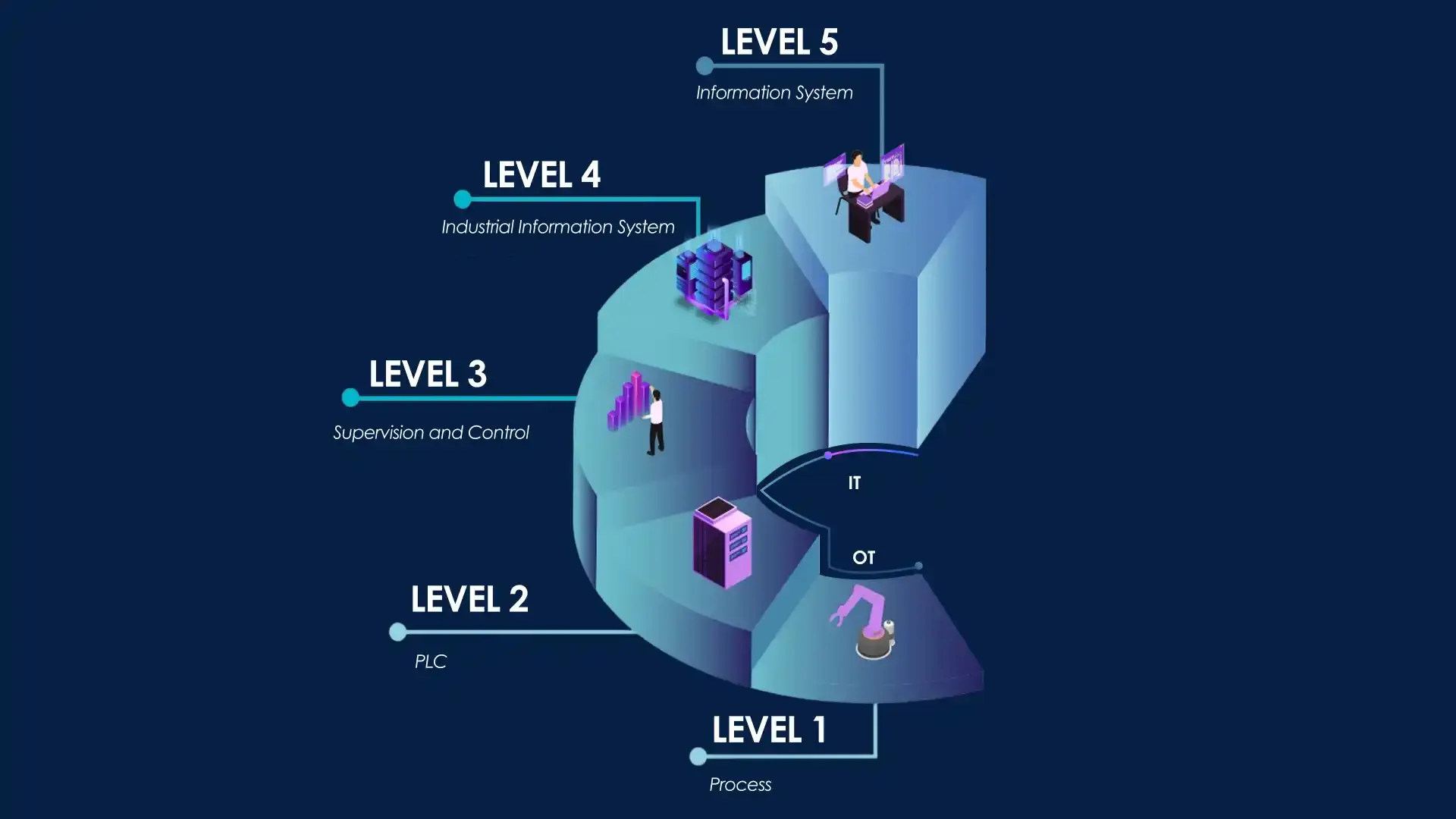
Implementing this model in your network infrastructure limits access to critical systems and reduces the attack surface for external threats. It also makes it easier to monitor and manage information flows.
Network segmentation is crucial to limiting the spread of attacks and protecting sensitive areas. While guaranteeing the continuity of industrial processes. It makes it possible to isolate key equipment, such as sensors, controllers, SCADA systems and PLCs. Industrial firewalls filter network flows according to criteria specific to industrial environments. These firewalls guarantee protection without disrupting the operation of industrial control systems.
Segmentation must also be accompanied by a more structured approach if it is to be fully effective.
One of the solutions used is the IDS probe (Intrusion Detection System), dedicated to network monitoring. The IDS probe performs an initial state of your network, serving as a basis for comparison. From this base, the probe will detect any anomalies and changes in behaviour on your industrial network. It identifies deviations from normal operation and alerts you to any threats. These alerts are crucial to protecting your critical systems and production lines. The IDS probe enhances your security and ensures optimum continuity of your operations.
Principle of least privilege
Applying the principle of least privilege ("Zero Trust" model) means granting each user only the rights necessary for their tasks.
- Identity control: Management of privileged accounts with identity and access management (IAM) solutions. Allows secure access to these sensitive accounts. Regular updating of passwords via a robust password policy to prevent leaks,
- Temporary access: Fixed-term permits for external service providers or one-off contributors,
- Access audit: Recording and tracking user activities with access monitoring solutions. Detection of any misuse. Access account review enables users' access rights to a system to be checked. It identifies inactive, obsolete or unauthorised accounts. It also ensures that access is properly segmented according to roles and responsibilities.
This strategy minimises the risk of account compromise.
Specialised security solutions
In addition to the solutions described above, DATIVE offers you tailor-made services:
- Mapping your industrial infrastructure: as a complement to an inventory, DATIVE can help you draw up a physical and logical map of your assets. Having a global view of your interconnections is essential for identifying vulnerabilities. The solutions put in place must be adapted to your infrastructure,
- Cybersecurity assessment: identify the vulnerabilities of your industrial control systems, measure the resilience of your infrastructure, prepare responses to incidents. All these solutions enable you to anticipate and minimise risks and improve security controls. Carry out a security audit on your infrastructure and prevent any attack that could neutralise your business,
- Integration and deployment of solutions: the cybersecurity solutions proposed may include the implementation of specialised products and tools. These deployments can be complex, resulting in poor protection and risk management. DATIVE will support you throughout the implementation process to ensure that deployment is secure and controlled.
Contact our experts for more information.
Conclusion
The security of industrial control systems is based on in-depth risk management. The solutions proposed must be adapted to industrial infrastructures. An integrated and proactive approach is crucial to ensure integrity, availability and resilience of industrial infrastructures.
With its expertise in industrial cybersecurity, DATIVE plays a key role in securing complex infrastructures. Despite the implementation of cybersecurity services and solutions, operators remain essential in maintaining control of their infrastructure.
For more information about our solutions and services, please contact us.





