ISO 50001: implementing an EMS to monitor and optimize your energy consumption
In today’s economic and environmental context, energy performance according to the NF EN ISO 50001 standard is an effective lever for controlling business costs. It helps reduce energy bills and leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions, also enabling organizations to contribute to their environmental and societal commitments. The ISO 50001 standard is therefore a strategic solution for optimizing energy management.
ISO 50001: requirements and compliance for optimized energy performance with an EMS | DATIVE
This article explores legal obligations, the sectors concerned, the requirements of the standard, and the key steps to ensure compliance. It also presents the benefits and challenges of ISO 50001, with support from DATIVE.
Objectives of the ISO 50001 standard
Main objectives
ISO 50001 establishes a methodical approach to help companies and organizations with high energy consumption structure and improve their energy management. Based on an Energy Management System (EMS), the standard provides a rigorous framework for monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing the use of energy resources, thus promoting more efficient and sustainable management.
The main objectives of ISO 50001 are:
- Continuous improvement of energy performance: the standard encourages companies to adopt a structured approach to optimize their energy consumption.
- Reduction of energy costs: by following ISO 50001 guidelines, companies can identify waste and implement corrective actions.
- Lower carbon footprint: by reducing energy consumption, companies contribute to climate goals and societal responsibility commitments.
- Integration into business strategy: the standard facilitates alignment of energy policies with the organization's strategic goals.
- Regulatory compliance: it ensures companies meet legal requirements in terms of energy efficiency, allowing them to anticipate regulatory changes and protect themselves from mandatory audits (see FAQ).
- Lower carbon footprint: by reducing energy consumption, companies contribute to climate goals and societal responsibility commitments.
- Stakeholder engagement: it promotes awareness and involvement of employees, suppliers, and customers in the company’s energy efforts.
- Access to subsidies and funding: ISO 50001 certification can strengthen the energy management structure, indirectly facilitating access to financial aid and Energy Savings Certificates (ESCs).

Target audience
The NF EN ISO 50001 standard targets a wide audience, including businesses of all sizes, public authorities, and private institutions. It is particularly relevant for industries, high energy consumers, and organizations seeking to optimize their energy usage.
Expected impact of compliance
Companies that adopt ISO 50001 benefit from several concrete advantages. By optimizing their energy consumption, they:
- achieve substantial savings on their energy bills
- significantly reduce their CO2 emissions
- and strengthen their commitment to sustainable development
This compliance is part of a broader dynamic driven by the State, particularly through programs such as PACTE Industrie and ADEME support schemes, which encourage companies to adopt more responsible energy practices.
Scope of the ISO 50001 standard
Sectors concerned
ISO 50001 applies to a wide range of sectors, including industry, healthcare, transportation, service buildings, and critical infrastructure. It is also relevant for large production companies, local authorities, and SMEs seeking to improve energy efficiency.
Types of organizations or activities targeted
All companies, regardless of their size and activity, can adopt this standard to structure and optimize their energy management. It is especially beneficial for organizations with significant energy consumption.
Technical or geographical scope
ISO 50001 is an international standard applicable to any organization, regardless of location. Its technical scope requires that the energy management system covers at least 80% of the organization’s energy bills.
Overview of ISO 50001 requirements and chapters
Implementing an Energy Management System (EMS)
ISO 50001 relies on the implementation of a structured EMS to manage, monitor, and improve energy performance within an organization. It defines processes to measure, monitor, and control energy consumption while establishing continuous improvement plans. Read our article on the topic.
Defining energy objectives
Companies must establish objectives and targets for energy management. These goals must be realistic, measurable, and aligned with the organization's overall strategy.
Monitoring and analyzing energy performance
ISO 50001 requires strict monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) related to energy consumption. This includes the use of measurement tools, energy data analysis, and identifying opportunities for improvement.
Action plan and continuous improvement
One of the core principles of ISO 50001 is the continuous improvement of energy performance through the PDCA cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act). This process ensures ongoing energy efficiency and lasting results.
Management commitment and stakeholder involvement
Implementing this standard requires strong commitment from management and involvement of teams. Raising employee awareness of good practices and energy management is essential to ensure EMS success.

Implementation and compliance with the ISO 50001 standard
Key steps for compliance
The ISO 50001 standard relies on the PDCA cycle to ensure continuous improvement of energy performance:
- Plan: appoint an Energy Manager, define an energy charter with clear objectives, and prioritize significant energy uses (SEUs).
- Do: implement the defined actions, allocate necessary resources, and deploy an Energy Management System (EMS) to structure efforts.
- Check: monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to validate results and measure the effectiveness of actions using technological tools.
- Act: adjust strategies, correct detected anomalies, and define new objectives to keep progressing.
A well-structured EMS ensures optimal energy management and enables companies to sustainably reduce costs while enhancing regulatory compliance.
Best practices
To ensure the effectiveness of ISO 50001, companies must adopt tools and methods suited to their activities. A high-performing EMS is based on:
- An adapted technological infrastructure: use of smart sensors, connected meters, and energy analysis software.
- Real-time monitoring: identifying key consumption areas and implementing alerts to detect anomalies.
- Expert support: assistance from specialized consultants to ensure compliance and optimize the EMS.
- Team involvement: training and awareness of energy efficiency to foster a culture of continuous improvement.
DATIVE, expert in energy management, offers a turnkey solution to meet EMS requirements through DAT’POWER, a platform designed to structure, optimize, and continuously monitor corporate energy performance.
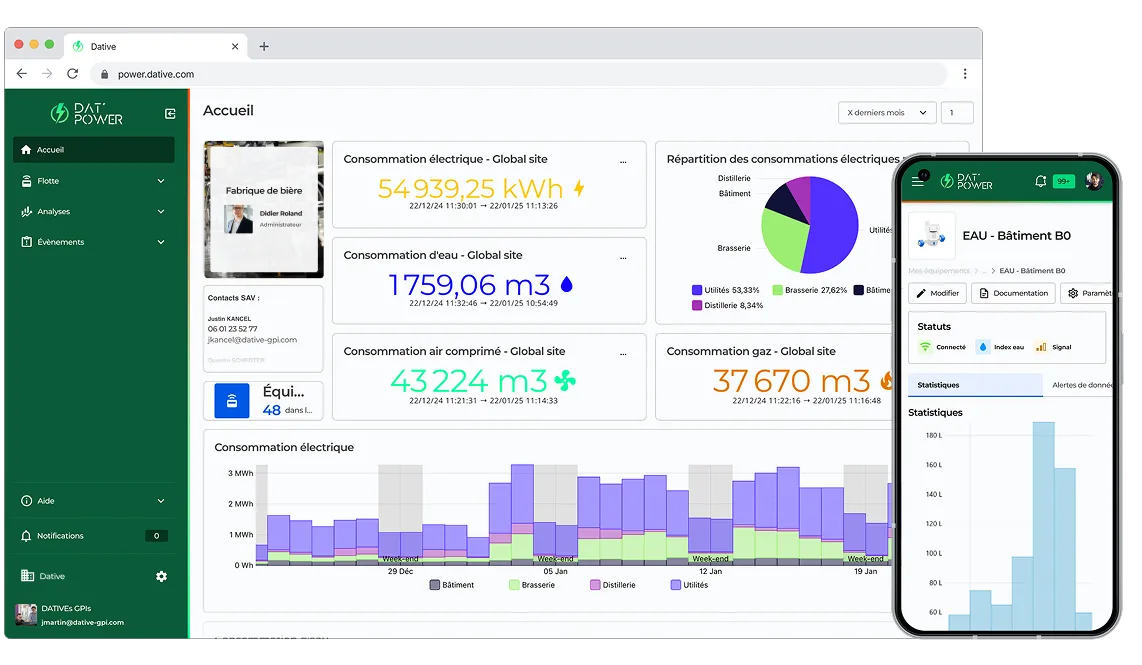
Available resources and tools
DATIVE offers companies personalized support for EMS implementation, providing tailored solutions:
- Integrated and optimized multisite management: facilitating rights management, reporting (audit, PSH, tertiary decree, BACS), and data analysis (data correlation / IPE...).
- Customized support: covering all project phases and adaptable based on the site's maturity.
- Real-time monitoring and effective data centralization: via our interoperable, multi-source, multi-protocol, and multi-energy platform (integration of your existing tools/equipment).
- Advanced alert system: enabling anomaly detection and leak identification through notifications, SMS, emails, etc.
- On-site expertise: installation of submeters and sensors using reliable, open equipment from recognized suppliers (Socomec, Adeunis, Itron, Tektelic, Endress+Hauser, etc.).
- A robust and scalable solution: integrating new features, regulatory tracking, and advances in AI and LLMs for increasingly optimized energy management.
Thanks to the expertise of the Gérard Perrier Industrie group, DATIVE helps you turn energy management into a strategic and sustainable lever for your company.
Choose a high-performing and scalable EMS with Dative!
Relationship with other standards
Complementary or related standards
ISO 50001 was developed based on the same principles as ISO 14001, thus facilitating their integration into a global management system.
Here is a list of related standards:
- ISO 14001 (Environment): covers all environmental impacts, including energy consumption, aiming to reduce resource depletion and emissions. However, ISO 14001 certification does not exempt companies from the mandatory energy audit.
- BACS Decree (Building Automation & Control Systems): requires the installation of building management systems (BMS) to optimize energy consumption in tertiary buildings.
- Tertiary Decree: requires tertiary buildings to gradually reduce their energy consumption, with specific targets to be met by 2050. Industrial players may also be concerned.
- APER Decree (Enhanced Energy Savings Audit and Plan): strengthens energy audit obligations for high-consuming companies and requires an action plan to improve their energy performance.
Comparison with other standards
ISO 50001 stands out from other energy efficiency standards thanks to its structured and certifiable approach. Unlike national standards, it offers international recognition.
Evolution and current developments
Version history and updates
- ISO 50001:2011: first version introduced to help companies structure and improve their energy management through an Energy Management System (EMS).
- ISO 50001:2018: major update incorporating the High-Level Structure (HLS), facilitating integration with other management standards such as ISO 9001 and ISO 14001. It also reinforces monitoring and continuous improvement requirements.
Future trends
- Digitalization and IoT: development of connected technologies for real-time energy monitoring, enabling more proactive and accurate management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and LLMs (Large Language Models): advanced use of energy data through AI and language models to identify optimizations and automate decision-making.
- Stronger regulatory requirements: progressive alignment with international climate goals (Paris Agreement, Fit for 55, CSRD) to promote a faster and more ambitious energy transition.
- Increased interoperability: development of solutions compatible with multiple protocols and platforms for integrated energy management across multi-site and multi-energy environments.
- Automation and predictive models: increasing integration of predictive algorithms to anticipate energy drifts and optimize real-time performance.
Benefits and challenges of the ISO 50001 standard
Benefits for companies
- Cost reduction: optimized energy management enables savings of 10 to 20% on bills.
- Lower carbon impact: reduced CO2 emissions and stronger climate commitment.
- Competitive advantage: a certification that highlights sustainable engagement to clients and partners.
- Quick return on investment: savings achieved quickly offset implementation costs.
- Increased competitiveness: lower energy expenses for more profitability and innovation.
- Regulatory compliance: anticipates legal developments and avoids obligations like mandatory energy audits.
- Stakeholder engagement: raises awareness and involves employees, suppliers, and clients in responsible energy practices.
- Facilitated access to ESC subsidies: setting up IPE performance indicators is easier with an EMS tool and allows access to ESCs via IND-UT-134 form.
Challenges or limitations
Although ISO 50001 offers many advantages, its implementation may present some challenges:
- Initial investment: the costs of setting up an EMS and obtaining certification can be a barrier for some companies.
- Organizational change: the standard requires internal process adaptation, which involves staff awareness and training.
- Ongoing monitoring: consistent tracking of energy performance is needed to ensure continuous improvement.
- Time commitment from teams: compliance requires significant internal involvement, demanding dedicated time and human resources.
Resources and references
To deepen your understanding of ISO 50001 and receive effective support for its implementation, here are some useful resources:
- Official ISO website: detailed presentation of the standard and its updates - ISO 50001 - Energy Management
- Ministry for the Ecological Transition: official information on public policies and measures related to improving energy performance - NF ISO 50001 Standard and Energy Performance
- ADEME (Agency for Ecological Transition): supports companies with financial aid for energy optimization and EMS implementation. Also discover their detailed guide on deploying an Energy Management System according to ISO 50001: Implementing an EMS according to ISO 50001.
FAQ
Question 1: Is ISO 50001 mandatory?
No, but some companies may be encouraged to adopt it to meet regulatory requirements or access funding.
Question 2: How long does it take to get certified?
This depends on the company’s size and complexity, but on average it takes between 6 and 12 months.
Question 3: What is the average return on investment?
The savings achieved generally allow payback within 2 to 5 years depending on the actions implemented.
Question 4: Is an energy audit mandatory without ISO 50001 certification?
Yes, for large companies (over 250 employees, turnover above €50M or balance sheet over €43M), an energy audit is mandatory every 4 years according to NF EN 16247. In case of non-compliance, companies risk financial penalties of up to 2% of their turnover, and 4% in case of repeat offenses, imposed by the DREAL.
Question 5: Is ISO 50001 certification an alternative to the energy audit?
Yes, ISO 50001 certification is considered an alternative to the NF EN 16247 energy audit.





